Anatomy of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis in adults: a pictorial essay with a multimodality approach
- PMID: 21108526
- PMCID: PMC3039176
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01302.x
Anatomy of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis in adults: a pictorial essay with a multimodality approach
Abstract
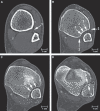
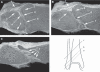
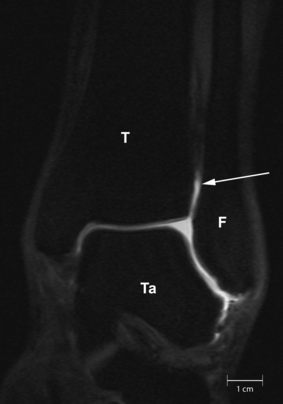
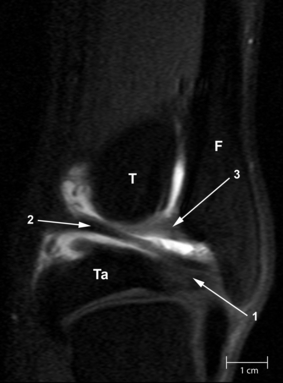
A syndesmosis is defined as a fibrous joint in which two adjacent bones are linked by a strong membrane or ligaments.This definition also applies for the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis, which is a syndesmotic joint formed by two bones and four ligaments. The distal tibia and fibula form the osseous part of the syndesmosis and are linked by the distal anterior tibiofibular ligament, the distal posterior tibiofibular ligament, the transverse ligament and the interosseous ligament. Although the syndesmosis is a joint, in the literature the term syndesmotic injury is used to describe injury of the syndesmotic ligaments. In an estimated 1–11% of all ankle sprains, injury of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis occurs. Forty percent of patients still have complaints of ankle instability 6 months after an ankle sprain. This could be due to widening of the ankle mortise as a result of increased length of the syndesmotic ligaments after acute ankle sprain. As widening of the ankle mortise by 1 mm decreases the contact area of the tibiotalar joint by 42%, this could lead to instability and hence early osteoarthritis of the tibiotalar joint. In fractures of the ankle, syndesmotic injury occurs in about 50% of type Weber B and in all of type Weber C fractures. However,in discussing syndesmotic injury, it seems the exact proximal and distal boundaries of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis are not well defined. There is no clear statement in the Ashhurst and Bromer etiological, the Lauge-Hansen genetic or the Danis-Weber topographical fracture classification about the exact extent of the syndesmosis. This joint is also not clearly defined in anatomical textbooks, such as Lanz and Wachsmuth. Kelikian and Kelikian postulate that the distal tibiofibular joint begins at the level of origin of the tibiofibular ligaments from the tibia and ends where these ligaments insert into the fibular malleolus. As the syndesmosis of the ankle plays an important role in the stability of the talocrural joint, understanding of the exact anatomy of both the osseous and ligamentous structures is essential in interpreting plain radiographs, CT and MR images, in ankle arthroscopy and in therapeutic management. With this pictorial essay we try to fill the hiatus in anatomic knowledge and provide a detailed anatomic description of the syndesmotic bones with the incisura fibularis, the syndesmotic recess, synovial fold and tibiofibular contact zone and the four syndesmotic ligaments. Each section describes a separate syndesmotic structure, followed by its clinical relevance and discussion of remaining questions.
© 2010 The Authors. Journal of Anatomy © 2010 Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures





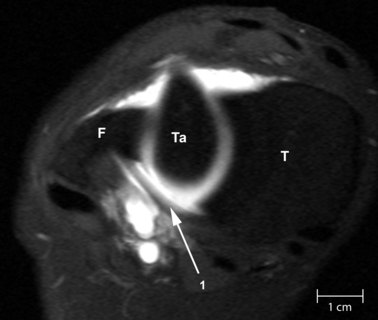
References
-
- Akseki D, Pinar H, Bozkurt M, et al. The distal fascicle of the anterior inferior tibio-fibular ligament as a cause of anterolateral ankle impingement: results of arthroscopic resection. Acta Orthop Scand. 1999;70:478–482. - PubMed
-
- Akseki D, Pinar H, Yaldiz K, et al. The anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament and talar impingement: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002;10:321–326. - PubMed
-
- Arner O, Ekengren K, Hulting B, et al. Arthrography of the talocrural joint: anatomic, roentgenographic, and clinical aspects. Acta Chir Scand. 1957;113:253–259. - PubMed
-
- Ashhurst APC, Bromer RS. Classification and mechanism of fractures of the leg bones involving the ankle: based on a study of three hundred cases from Episcopal Hospital. Arch Surg. 1922;4:51–129.
-
- Bartonicek J. Anatomy of the tibiofibular syndesmosis and its clinical relevance. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003;25:379–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

