Prosthetic overhang is the most effective way to prevent scapular conflict in a reverse total shoulder prosthesis
- PMID: 21110704
- PMCID: PMC3216083
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2010.538354
Prosthetic overhang is the most effective way to prevent scapular conflict in a reverse total shoulder prosthesis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Despite good clinical results with the reverse total shoulder arthroplasty, inferior scapular notching remains a concern. We evaluated 6 different solutions to overcome the problem of scapular notching.
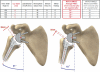
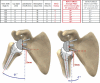
Methods: An average and a "worst case scenario" shape in A-P view in a 2-D computer model of a scapula was created, using data from 200 "normal" scapulae, so that the position of the glenoid and humeral component could be changed as well as design features such as depth of the polyethylene insert, the size of glenosphere, the position of the center of rotation, and downward glenoid inclination. The model calculated the maximum adduction (notch angle) in the scapular plane when the cup of the humeral component was in conflict with the scapula.
Results: A change in humeral neck shaft inclination from 155° to 145° gave a 10° gain in notch angle. A change in cup depth from 8 mm to 5 mm gave a gain of 12°. With no inferior prosthetic overhang, a lateralization of the center of rotation from 0 mm to 5 mm gained 16°. With an inferior overhang of only 1 mm, no effect of lateralizing the center of rotation was noted. Downward glenoid inclination of 0º to 10º gained 10°. A change in glenosphere radius from 18 mm to 21 mm gained 31° due to the inferior overhang created by the increase in glenosphere. A prosthetic overhang to the bone from 0 mm to 5 mm gained 39°.
Interpretation: Of all 6 solutions tested, the prosthetic overhang created the biggest gain in notch angle and this should be considered when designing the reverse arthroplasty and defining optimal surgical technique.
Figures








References
-
- Boileau P, Watkinson DJ, Hatzidakis AM, Balg F. Grammont reverse prosthesis: design, rationale, and biomechanics. J Shoulder Elbow Surg (Suppl S) 2005;14((1)):147S–161S. - PubMed
-
- Boileau P, Watkinson DJ, Hatzidakis AM, Hovorka I. Neer Award 2005: The Grammont reverse shoulder prosthesis: Results in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15:527–40. - PubMed
-
- Chou J, Malak SF, Anderson IA, Astley T, Poon PP. Biomechanical evaluation of different designs of glenospheres in the SMR reverse total shoulder prosthesis: Range of motion and risk of scapular notching. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18:354–9. - PubMed
-
- De Wilde LF, Audenaert EA, Berghs BM. Shoulder prostheses treating cuff tear arthropathy: a comparative biomechanical study. J Orthop Res. 2004;22((6)):1222–30. - PubMed
-
- De Wilde LF, Plasschaert FS, Audenaert EA, Verdonk RC. Functional recovery after a reverse prosthesis for reconstruction of the proximal humerus in tumor surgery. Clin Orthop. 2005;((430)):156–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
