In Lysinuric Protein Intolerance system y+L activity is defective in monocytes and in GM-CSF-differentiated macrophages
- PMID: 21110863
- PMCID: PMC2999609
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-5-32
In Lysinuric Protein Intolerance system y+L activity is defective in monocytes and in GM-CSF-differentiated macrophages
Abstract
Background: In the recessive aminoaciduria Lysinuric Protein Intolerance (LPI), mutations of SLC7A7/y+LAT1 impair system y+L transport activity for cationic amino acids. A severe complication of LPI is a form of Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP), in which alveolar spaces are filled with lipoproteinaceous material because of the impaired surfactant clearance by resident macrophages. The pathogenesis of LPI-associated PAP remains still obscure. The present study investigates for the first time the expression and function of y+LAT1 in monocytes and macrophages isolated from a patient affected by LPI-associated PAP. A comparison with mesenchymal cells from the same subject has been also performed.
Methods: Monocytes from peripheral blood were isolated from a 21-year-old patient with LPI. Alveolar macrophages and fibroblastic-like mesenchymal cells were obtained from a whole lung lavage (WLL) performed on the same patient. System y+L activity was determined measuring the 1-min uptake of [3H]-arginine under discriminating conditions. Gene expression was evaluated through qRT-PCR.
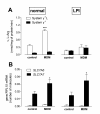
Results: We have found that: 1) system y+L activity is markedly lowered in monocytes and alveolar macrophages from the LPI patient, because of the prevailing expression of SLC7A7/y+LAT1 in these cells; 2) on the contrary, fibroblasts isolated from the same patient do not display the transport defect due to compensation by the SLC7A6/y+LAT2 isoform; 3) in both normal and LPI monocytes, GM-CSF induces the expression of SLC7A7, suggesting that the gene is a target of the cytokine; 4) GM-CSF-induced differentiation of LPI monocytes is comparable to that of normal cells, demonstrating that GM-CSF signalling is unaltered; 5) general and respiratory conditions of the patient, along with PAP-associated parameters, markedly improved after GM-CSF therapy through aerosolization.
Conclusions: Monocytes and macrophages, but not fibroblasts, derived from a LPI patient clearly display the defect in system y+L-mediated arginine transport. The different transport phenotypes are referable to the relative levels of expression of SLC7A7 and SLC7A6. Moreover, the expression of SLC7A7 is regulated by GM-CSF in monocytes, pointing to a role of y+LAT1 in the pathogenesis of LPI associated PAP.
Figures


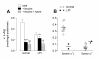



References
-
- Torrents D, Estevez R, Pineda M, Fernandez E, Lloberas J, Shi YB, Zorzano A, Palacin M. Identification and characterization of a membrane protein (y+L amino acid transporter-1) that associates with 4F2 hc to encode the amino acid transport activity y+L. A candidate gene for lysinuric protein intolerance. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:32437–32445. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.49.32437. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

