How does cAMP/protein kinase A signaling lead to tumors in the adrenal cortex and other tissues?
- PMID: 21111774
- PMCID: PMC3049838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.11.018
How does cAMP/protein kinase A signaling lead to tumors in the adrenal cortex and other tissues?
Abstract
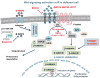
The overwhelming majority of benign lesions of the adrenal cortex leading to Cushing syndrome are linked to one or another abnormality of the cAMP signaling pathway. A small number of both massive macronodular adrenocortical disease and cortisol-producing adenomas harbor somatic GNAS mutations. Micronodular adrenocortical hyperplasias are either pigmented (the classic form being that of primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease) or non-pigmented; micronodular adrenocortical hyperplasias can be seen in the context of other conditions or isolated; for example, primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease usually occurs in the context of Carney complex, but isolated primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease has also been described. Both Carney complex and isolated primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease are caused by germline PRKAR1A mutations; somatic mutations of this gene that regulates cAMP-dependent protein kinase are also found in cortisol-producing adenomas, and abnormalities of PKA are present in most cases of massive macronodular adrenocortical disease. Micronodular adrenocortical hyperplasias and some cortisol-producing adenomas are associated with phosphodiesterase 11A and 8B defects, coded, respectively, by the PDE11A and PDE8B genes. Mouse models of Prkar1a deficiency also show that increased cAMP signaling leads to tumors in adrenal cortex and other tissues. In this review, we summarize all recent data from ours and other laboratories, supporting the view that Wnt-signaling acts as an important mediator of tumorigenicity induced by abnormal PRKAR1A function and aberrant cAMP signaling.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Almeida MQ, Muchow M, Boikos S, Bauer AJ, Griffin KJ, Tsang KM, Cheadle C, Watkins T, Wen F, Starost MF, Bossis I, Nesterova M, Stratakis CA. Mouse Prkar1a haploinsufficiency leads to an increase in tumors in the Trp53+/- or Rb1+/- backgrounds and chemically induced skin papillomas by dysregulation of the cell cycle and Wnt signaling. Hum Mol Genet. 2010a;19:1387–1398. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almeida MQ, Tsang KM, Cheadle C, Watkins T, Grivel JC, Nesterova M, Goldbach-Mansky R, Stratakis CA. Protein kinase A regulates caspase-1 via Ets-1 in bone stromal cell-derived lesions: a link between cyclic AMP and pro-inflammatory pathways in osteoblast progenitors. Hum Mol Genet. 2010b in press. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertherat J, Groussin L, Sandrini F, Matyakhina L, Bei T, Stergiopoulos S, Papageorgiou T, Bourdeau I, Kirschner LS, Vincent-Dejean C, Perlemoine K, Gicquel C, Bertagna X, Stratakis CA. Molecular and functional analysis of PRKAR1A and its locus (17q22-24) in sporadic adrenocortical tumors: 17q losses, somatic mutations, and protein kinase A expression and activity. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5308–5319. - PubMed
-
- Bertherat J, Horvath A, Groussin L, Grabar S, Boikos S, Cazabat L, Libe R, Rene-Corail F, Stergiopoulos S, Bourdeau I, Bei T, Clauser E, Calender A, Kirschner LS, Bertagna X, Carney JA, Stratakis CA. Mutations in regulatory subunit type 1A of cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase (PRKAR1A): phenotype analysis in 353 patients and 80 different genotypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:2085–2091. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

