Molecular imaging of the kidneys
- PMID: 21111857
- PMCID: PMC3002465
- DOI: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2010.09.003
Molecular imaging of the kidneys
Abstract
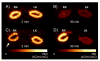
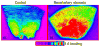
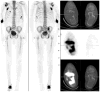
Radionuclide imaging of the kidneys with gamma cameras involves the use of labeled molecules seeking functionally critical molecular mechanisms to detect the pathophysiology of the diseased kidneys and achieve an early, sensitive, and accurate diagnosis. The most recent imaging technology, positron emission tomography, permits quantitative imaging of the kidney at a spatial resolution appropriate for the organ. H(2)(15)O, (82)RbCl, and [(64)Cu] ETS are the most important radiopharmaceuticals for measuring renal blood flow. The renin angiotensin system is the most important regulator of renal blood flow; this role is being interrogated by detecting angiotensin receptor subtype angiotensin subtype 1 receptor by the use of in vivo positron emission tomography. Membrane organic anion transporters are important for the function of the tubular epithelium; therefore, Tc99m MAG3 as well as some novel radiopharmaceuticals, such as copper-64 labeled mono oxo-tetraazamacrocyclic ligands, have been used for molecular renal imaging. In addition, other radioligands that interact with the organic cation transporters or peptide transporters have been developed. Focusing on early detection of kidney injury at the molecular level is an evolving field of great significance. Potential imaging targets are the kidney injury molecule 1, which is highly expressed in kidney injury and renal cancer but not in normal kidneys. Although pelvic clearance, in addition to parenchymal transport, is an important measure in obstructive nephropathy, techniques that focus on up-regulated molecules in response to tissue stress resulting from obstruction will be of great implication. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is a well-suited molecule here. The greatest advances in molecular imaging of the kidneys have been recently achieved in detecting renal cancer. In addition to the ubiquitous [(18)F] fluorodeoxyglucose, other radioligands, such as [(11)C] acetate and anti-1-amino-3-[18F]fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid, have emerged. Radioimmunoimaging with [(124)I] G250 could lead to radioimmunotherapy for renal cancer. Considering the increasing age of general population, the incidence of kidney diseases, such as atherosclerosis, diabetic nephropathy, and cancer, is expected to increase. Successful management of these diseases offers an opportunity and a challenge for development of novel molecular imaging technologies.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- GLIMSTEDT G. Some recent views on the structure and function of the kidney. Bull Schweiz Akad Med Wiss. 1947;3(23):182–195. - PubMed
-
- DRENCKHAHN FO, MEISSNER J. Autoradiographic studies on the localization of S35 labelled Na2SO4 in the kidney of guinea pigs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1956;227(5):444–455. - PubMed
-
- zum WINKEL K, SCHEER KE. Principles of kidney scintigraphy with Hg-203 labelled Salyrgan. Nucl Med (Stuttg) 1961;2:71–79. - PubMed
-
- Stadalnik RC, Vogel JM, Jansholt AL, et al. Renal clearance and extraction parameters of ortho-iodohippurate (I-123) compared with OIH(I-131) and PAH. J Nucl Med. 1980;21(2):168–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

