Evidence for SMAD3 as a modifier of breast cancer risk in BRCA2 mutation carriers
- PMID: 21114847
- PMCID: PMC3046447
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2785
Evidence for SMAD3 as a modifier of breast cancer risk in BRCA2 mutation carriers
Abstract
Introduction: Current attempts to identify genetic modifiers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 associated risk have focused on a candidate gene approach, based on knowledge of gene functions, or the development of large genome-wide association studies. In this study, we evaluated 24 SNPs tagged to 14 candidate genes derived through a novel approach that analysed gene expression differences to prioritise candidate modifier genes for association studies.
Methods: We successfully genotyped 24 SNPs in a cohort of up to 4,724 BRCA1 and 2,693 BRCA2 female mutation carriers from 15 study groups and assessed whether these variants were associated with risk of breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers.
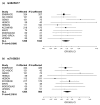
Results: SNPs in five of the 14 candidate genes showed evidence of association with breast cancer risk for BRCA1 or BRCA2 carriers (P < 0.05). Notably, the minor alleles of two SNPs (rs7166081 and rs3825977) in high linkage disequilibrium (r² = 0.77), located at the SMAD3 locus (15q22), were each associated with increased breast cancer risk for BRCA2 mutation carriers (relative risk = 1.25, 95% confidence interval = 1.07 to 1.45, P(trend) = 0.004; and relative risk = 1.20, 95% confidence interval = 1.03 to 1.40, P(trend) = 0.018).
Conclusions: This study provides evidence that the SMAD3 gene, which encodes a key regulatory protein in the transforming growth factor beta signalling pathway and is known to interact directly with BRCA2, may contribute to increased risk of breast cancer in BRCA2 mutation carriers. This finding suggests that genes with expression associated with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation status are enriched for the presence of common genetic modifiers of breast cancer risk in these populations.
Figures
References
-
- Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Loman N, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, Pasini B, Radice P, Manoukian S, Eccles DM, Tang N, Olah E, Anton-Culver H, Warner E, Lubinski J, Gronwald J, Gorski B, Tulinius H, Thorlacius S, Eerola H, Nevanlinna H, Syrjakoski K, Kallioniemi OP, Thompson D, Evans C, Peto J. et al. Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case Series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72:1117–1130. doi: 10.1086/375033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Iversen ES, Friebel T, Finkelstein D, Weber BL, Eisen A, Peterson LE, Schildkraut JM, Isaacs C, Peshkin BN, Corio C, Leondaridis L, Tomlinson G, Dutson D, Kerber R, Amos CI, Strong LC, Berry DA, Euhus DM, Parmigiani G. Characterization of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in a large United States sample. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:863–871. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.03.6772. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Milne RL, Osorio A, Cajal TR, Vega A, Llort G, de la Hoya M, Diez O, Alonso MC, Lazaro C, Blanco I, Sanchez-de-Abajo A, Caldes T, Blanco A, Grana B, Duran M, Velasco E, Chirivella I, Cardenosa EE, Tejada MI, Beristain E, Miramar MD, Calvo MT, Martinez E, Guillen C, Salazar R, San Roman C, Antoniou AC, Urioste M, Benitez J. The average cumulative risks of breast and ovarian cancer for carriers of mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 attending genetic counseling units in Spain. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2861–2869. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4436. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

