Signaling role of Cdc42 in regulating mammalian physiology
- PMID: 21115489
- PMCID: PMC3024731
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R110.200329
Signaling role of Cdc42 in regulating mammalian physiology
Abstract
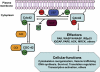
Cdc42 is a member of the Rho GTPase family of intracellular molecular switches regulating multiple signaling pathways involved in actomyosin organization and cell proliferation. Knowledge of its signaling function in mammalian cells came mostly from studies using the dominant-negative or constitutively active mutant overexpression approach in the past 2 decades. Such an approach imposes a number of experimental limitations related to specificity, dosage, and/or clonal variability. Recent studies by conditional gene targeting of cdc42 in mice have revealed its tissue- and cell type-specific role and provide definitive information of the physiological signaling functions of Cdc42 in vivo.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

