Utility of ultrasound joint counts in the prediction of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with very early synovitis
- PMID: 21115552
- PMCID: PMC3033529
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.131573
Utility of ultrasound joint counts in the prediction of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with very early synovitis
Abstract
Objectives: Early therapy improves outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It is therefore important to improve predictive algorithms for RA in early disease. This study evaluated musculoskeletal ultrasound, a sensitive tool for the detection of synovitis and erosions, as a predictor of outcome in very early synovitis.
Methods: 58 patients with clinically apparent synovitis of at least one joint and symptom duration of ≤3 months underwent clinical, laboratory, radiographic and 38 joint ultrasound assessments and were followed prospectively for 18 months, determining outcome by 1987 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and 2010 ACR/European League Against Rheumatism criteria. Sensitivity and specificity for 1987 RA criteria were determined for ultrasound variables and logistic regression models were then fitted to evaluate predictive ability over and above the Leiden rule.
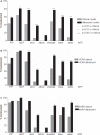
Results: 16 patients resolved, 13 developed non-RA persistent disease and 29 developed RA by 1987 criteria. Ultrasound demonstrated subclinical wrist, elbow, knee, ankle and metatarsophalangeal joint involvement in patients developing RA. Large joint and proximal interphalangeal joint ultrasound variables had poor predictive ability, whereas ultrasound erosions lacked specificity. Regression analysis demonstrated that greyscale wrist and metacarpophalangeal joint involvement, and power Doppler involvement of metatarsophalangeal joints provided independently predictive data. Global ultrasound counts were inferior to minimal power Doppler counts, which significantly improved area under the curve values from 0.905 to 0.962 combined with the Leiden rule.
Conclusion: In a longitudinal study, extended ultrasound joint evaluation significantly increased detection of joint involvement in all regions and outcome groups. Greyscale and power Doppler scanning of metacarpophalangeal joints, wrists and metatarsophalangeal joints provides the optimum minimal ultrasound data to improve on clinical predictive models for RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Finckh A, Liang MH, van Herckenrode CM, et al. Long-term impact of early treatment on radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum 2006;55:864–72 - PubMed
-
- Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, et al. Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004;43:906–14 - PubMed
-
- Möttönen T, Hannonen P, Korpela M, et al. Delay to institution of therapy and induction of remission using single-drug or combination-disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:894–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

