Intrarenal angiotensin-converting enzyme induces hypertension in response to angiotensin I infusion
- PMID: 21115616
- PMCID: PMC3060439
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010060624
Intrarenal angiotensin-converting enzyme induces hypertension in response to angiotensin I infusion
Abstract
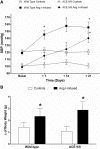
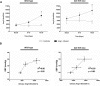
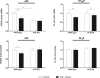
The contribution of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system to the development of hypertension is incompletely understood. Here, we used targeted homologous recombination to generate mice that express angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) in the kidney tubules but not in other tissues. Mice homozygous for this genetic modification (ACE 9/9 mice) had low BP levels, impaired ability to concentrate urine, and variable medullary thinning. In accord with the ACE distribution, these mice also had reduced circulating angiotensin II and high plasma renin concentration but maintained normal kidney angiotensin II levels. In response to chronic angiotensin I infusions, ACE 9/9 mice displayed increased kidney angiotensin II, enhanced rate of urinary angiotensin II excretion, and development of hypertension. These findings suggest that intrarenal ACE-derived angiotensin II formation, even in the absence of systemic ACE, increases kidney angiotensin II levels and promotes the development of hypertension.
Figures
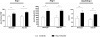
References
-
- Hansson L, Lindholm LH, Niskanen L, Lanke J, Hedner T, Niklason A, Luomanmaki K, Dahlof B, de Faire U, Morlin C, Karlberg BE, Wester PO, Bjorck JE: Effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition compared with conventional therapy on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: The Captopril Prevention Project (CAPPP) randomised trial. Lancet 353: 611–616, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Sleight P, Pogue J, Bosch J, Davies R, Dagenais G: Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 342: 145–153, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Giles TD: Renin-angiotensin system modulation for treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases: Toward an optimal therapeutic strategy. Rev Cardiovasc Med 8 [Suppl 2]: S14–S21, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Investigators O, Yusuf S, Teo KK, Pogue J, Dyal L, Copland I, Schumacher H, Dagenais G, Sleight P, Anderson C: Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N Engl J Med 358: 1547–1559, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Schmieder RE, Hilgers KF, Schlaich MP, Schmidt BM: Renin-angiotensin system and cardiovascular risk. Lancet 369: 1208–1219, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

