Preoperative proteinuria predicts adverse renal outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting
- PMID: 21115618
- PMCID: PMC3014044
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010050553
Preoperative proteinuria predicts adverse renal outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting
Abstract
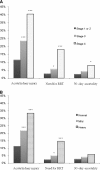
Whether preoperative proteinuria associates with adverse renal outcomes after cardiac surgery is unknown. Here, we performed a secondary analysis of a prospectively enrolled cohort of adult patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) at a medical center and its two affiliate hospitals between 2003 and 2007. We excluded patients with stage 5 CKD or those who received dialysis previously. We defined proteinuria, measured with a dipstick, as mild (trace to 1+) or heavy (2+ to 4+). Among a total of 1052 patients, cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury (CSA-AKI) developed in 183 (17.4%) patients and required renal replacement therapy (RRT) in 50 (4.8%) patients. In a multiple logistic regression model, mild and heavy proteinuria each associated with an increased odds of CSA-AKI, independent of CKD stage and the presence of diabetes mellitus (mild: OR 1.66, 95% CI 1.09 to 2.52; heavy: OR 2.30, 95% CI 1.35 to 3.90). Heavy proteinuria also associated with increased odds of postoperative RRT (OR 7.29, 95% CI 3.00 to 17.73). In summary, these data suggest that preoperative proteinuria is a predictor of CSA-AKI among patients undergoing CABG.
Figures

References
-
- Rosner MH, Okusa MD: Acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 19–32, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Lassnigg A, Schmidlin D, Mouhieddine M, Bachmann LM, Druml W, Bauer P, Hiesmayr M: Minimal changes of serum creatinine predict prognosis in patients after cardiothoracic surgery: A prospective cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1597–1605, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Klausen K, Borch-Johnsen K, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Jensen G, Clausen P, Scharling H, Appleyard M, Jensen JS: Very low levels of microalbuminuria are associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease and death independently of renal function, hypertension, and diabetes. Circulation 110: 32–35, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Mann JF, Gerstein HC, Pogue J, Bosch J, Yusuf S: Renal insufficiency as a predictor of cardiovascular outcomes and the impact of ramipril: The HOPE randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 134: 629–636, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Hillege HL, Fidler V, Diercks GF, van Gilst WH, de Zeeuw D, van Veldhuisen DJ, Gans RO, Janssen WM, Grobbee DE, de Jong PE: Urinary albumin excretion predicts cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality in general population. Circulation 106: 1777–1782, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

