MCP-induced protein 1 deubiquitinates TRAF proteins and negatively regulates JNK and NF-kappaB signaling
- PMID: 21115689
- PMCID: PMC3005225
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20092641
MCP-induced protein 1 deubiquitinates TRAF proteins and negatively regulates JNK and NF-kappaB signaling
Abstract
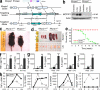
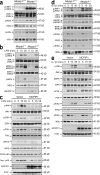
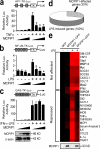
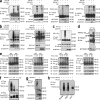
The intensity and duration of macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses are controlled by proteins that modulate inflammatory signaling pathways. MCPIP1 (monocyte chemotactic protein-induced protein 1), a recently identified CCCH Zn finger-containing protein, plays an essential role in controlling macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. However, its mechanism of action is poorly understood. In this study, we show that MCPIP1 negatively regulates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and NF-κB activity by removing ubiquitin moieties from proteins, including TRAF2, TRAF3, and TRAF6. MCPIP1-deficient mice spontaneously developed fatal inflammatory syndrome. Macrophages and splenocytes from MCPIP1(-/-) mice showed elevated expression of inflammatory gene expression, increased JNK and IκB kinase activation, and increased polyubiquitination of TNF receptor-associated factors. In vitro assays directly demonstrated the deubiquitinating activity of purified MCPIP1. Sequence analysis together with serial mutagenesis defined a deubiquitinating enzyme domain and a ubiquitin association domain in MCPIP1. Our results indicate that MCPIP1 is a critical modulator of inflammatory signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Deng L., Wang C., Spencer E., Yang L., Braun A., You J., Slaughter C., Pickart C., Chen Z.J.. 2000. Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell. 103:351–361. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00126-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hadari T., Warms J.V., Rose I.A., Hershko A.. 1992. A ubiquitin C-terminal isopeptidase that acts on polyubiquitin chains. Role in protein degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 267:719–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

