Characterization and online detection of surfactin isomers based on HPLC-MS(n) analyses and their inhibitory effects on the overproduction of nitric oxide and the release of TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS-induced macrophages
- PMID: 21116409
- PMCID: PMC2992995
- DOI: 10.3390/md8102605
Characterization and online detection of surfactin isomers based on HPLC-MS(n) analyses and their inhibitory effects on the overproduction of nitric oxide and the release of TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS-induced macrophages
Abstract
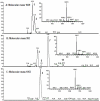
A rapid method for characterization and online detection of surfactin isomers was developed based on HPLC-MS(n) (n = 1, 2, 3) analyses, and many surfactin isomers were detected and characterized from the bioactive fraction of the mangrove bacterium Bacillus sp. Inhibitory activities of surfactin isomers on the overproduction of nitric oxide and the release of TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS-induced macrophages were systematically investigated. It was revealed that the surfactin isomers showed strong inhibitory properties on the overproduction of nitric oxide and the release of IL-6 on LPS-induced murine macrophage cell RAW264.7 with IC(50) values ranging from 1.0 to 7.0 μM. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies revealed that the existence of the free carboxyl group in the structure of surfactin isomers was crucial. These findings will be very helpful for the development of this novel kind of natural product as new anti-inflammatory agents.
Keywords: Bacillus sp.; LC-MS; anti-inflammatory activity; surfactin isomer.
Figures





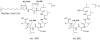
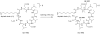
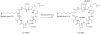
References
-
- Kikuchi T, Hasumi K. Enhancement of plasminogen activation by surfactin C: augmentation of fibrinolysis in vitro and in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2002;1596:234–245. - PubMed
-
- Wang CL, Ng TB, Yuan F, Liu ZK, Liu F. Induction of apoptosis in human leukemia K562 cells by cyclic lipopeptide from Bacillus subtilis natto T-2. Peptides. 2007;28:1344–1350. - PubMed
-
- Vollenbroich D, Ozel M, Vater J, Kamp RM, Pauli G. Mechanism of inactivation of enveloped viruses by the biosurfactant surfactin from Bacillus subtilis. Biologicals. 1997;25:289–297. - PubMed
-
- Kim K, Jung SY, Lee DK, Jung JK, Park JK, Kim DK, Lee CH. Suppression of inflammatory responses by surfactin, a selective inhibitor of platelet cytosolic phospholipase A(2) Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998;55:975–985. - PubMed
-
- Hwang MH, Lim JH, Yun HI, Rhee MH, Cho JY, Hsu W, Park SC. Surfactin C inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced transcription of interleukin-1 beta and inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide production in murine RAW264.7 cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005;27:1605–1608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
