Effects of Axial Stretch on Cell Proliferation and Intimal Thickness in Arteries in Organ Culture
- PMID: 21116478
- PMCID: PMC2992346
- DOI: 10.1007/s12195-010-0128-9
Effects of Axial Stretch on Cell Proliferation and Intimal Thickness in Arteries in Organ Culture
Abstract
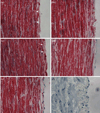
Intimal hyperplasia (IH) remains the major cause of intermediate and long-term failure of vascular grafts and endovascular interventions. Arteries are subjected to a significant longitudinal stress in addition to the shear stress and tensile stress from the blood flow. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of axial stretch on cell proliferation and IH in arteries. Porcine carotid arteries, intact or endothelial cell (EC) denudated, were maintained ex vivo at different stretch ratios (1.3, 1.5, and 1.8) and flow rates (16 or 160 mL/min) while remaining at physiologic pressure for 7 days. The viability of the arteries was verified with norepinephrine, carbachol, and sodium nitroprusside stimulations, and the cell proliferation was detected using bromodeoxyuridine labeling and immunostaining. Our results showed that the axial stretch ratio did not significantly affect intimal thickness and cell proliferation in normal arteries. However, axial stretch increased the neointimal thickness in EC denudated arteries cultured under low flow conditions. The cell proliferation increased significantly in the intima and inner half of the media of the EC denudated arteries under normal or elevated axial stretch in comparison to intact arteries at the same stretch ratio. These results demonstrated that axial stretch with EC denudation and low flow increases neointimal formation and cell proliferation in the arteries.
Figures






References
-
- Bayes-Genis A, Kantor B, Keelan PC, Altman JD, Lubbe DF, Kang JH, Schwartz RS. Restenosis and hyperplasia: animal models. Curr. Interv. Cardiol. Rep. 2000;2(4):303–308. - PubMed
-
- Boonen HC, Schiffers PM, Fazzi GE, Janssen GM, Daemen MJ, De Mey JG. DNA synthesis in isolated arteries. Kinetics and structural consequences. Am. J. Physiol. 1991;260(1 Pt 2):H210–H217. - PubMed
-
- Casterella PJ, Teirstein PS. Prevention of coronary restenosis. Cardiol. Rev. 1999;7(4):219–231. - PubMed
-
- Cheng CP, Wilson NM, Hallett RL, Herfkens RJ, Taylor CA. In vivo MR angiographic quantification of axial and twisting deformations of the superficial femoral artery resulting from maximum hip and knee flexion. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006;17(6):979–987. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

