MITF-siRNA formulation is a safe and effective therapy for human melasma
- PMID: 21119619
- PMCID: PMC3034856
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.263
MITF-siRNA formulation is a safe and effective therapy for human melasma
Abstract
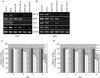
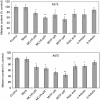
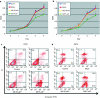
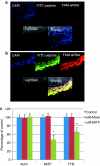
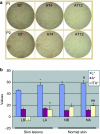
It is unclear whether siRNA-based agents can be a safe and effective therapy for diseases. In this study, we demonstrate that microphthalmia-associated transcription factor-siRNA (MITF-siR)-silenced MITF gene expression effectively induced a significant reduction in tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1, and melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) levels. The siRNAs caused obvious inhibition of melanin synthesis and melanoma cell apoptosis. Using a novel type of transdermal peptide, we developed the formulation of an MITF-siR cream. Results demonstrated that hyperpigmented facial lesions of siRNA-treated subjects were significantly lighter after 12 weeks of therapy than before treatment (P < 0.001); overall improvement was first noted after 4 weeks of siRNA treatment. At the end of treatment, clinical and colorimetric evaluations demonstrated a 90.4% lightening of the siRNA-treated lesions toward normal skin color. The relative melanin contents in the lesions and adjacent normal skin were decreased by 26% and 7.4%, respectively, after treatment with the MITF-siR formulation. Topical application of siRNA formulation significantly lightens brown facial hypermelanosis and lightens normal skin in Asian individuals. This treatment represents a safe and effective therapy for melasma, suggesting that siRNA-based agents could be developed for treating other diseases such as melanoma.
Figures


References
-
- Cestari T, Arellano I, Hexsel D., and, Ortonne JP, Latin American Pigmentary Disorders Academy Melasma in Latin America: options for therapy and treatment algorithm. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:760–772. - PubMed
-
- Gupta AK, Gover MD, Nouri K., and, Taylor S. The treatment of melasma: a review of clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:1048–1065. - PubMed
-
- Parvez S, Kang M, Chung HS, Cho C, Hong MC, Shin MK, et al. Survey and mechanism of skin depigmenting and lightening agents. Phytother Res. 2006;20:921–934. - PubMed
-
- Rafal ES, Griffiths CE, Ditre CM, Finkel LJ, Hamilton TA, Ellis CN, et al. Topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) treatment for liver spots associated with photodamage. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:368–374. - PubMed
-
- Stern RS. Clinical practice. Treatment of photoaging. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1526–1534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

