Deubiquitinases in the regulation of NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 21119682
- PMCID: PMC3075605
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2010.166
Deubiquitinases in the regulation of NF-κB signaling
Abstract
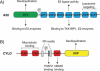
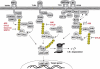
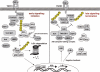
Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is a critical regulator of multiple biological functions including innate and adaptive immunity and cell survival. Activation of NF-κB is tightly regulated to preclude chronic signaling that may lead to persistent inflammation and cancer. Ubiquitination of key signaling molecules by E3 ubiquitin ligases has emerged as an important regulatory mechanism for NF-κB signaling. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) counteract E3 ligases and therefore play a prominent role in the downregulation of NF-κB signaling and homeostasis. Understanding the mechanisms of NF-κB downregulation by specific DUBs such as A20 and CYLD may provide therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:693–733. - PubMed
-
- Chen LF, Greene WC. Shaping the nuclear action of NF-κB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S, Hayden MS. New regulators of NF-κB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:837–848. - PubMed
-
- Scheidereit C. IκB kinase complexes: gateways to NF-κB activation and transcription. Oncogene. 2006;25:6685–6705. - PubMed
-
- Bours V, Franzoso G, Azarenko V, et al. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly transactivates through κB motifs via association with DNA-binding p50 homodimers. Cell. 1993;72:729–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

