The use of exogenous melatonin in delayed sleep phase disorder: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 21120122
- PMCID: PMC2982730
- DOI: 10.1093/sleep/33.12.1605
The use of exogenous melatonin in delayed sleep phase disorder: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Study objectives: To perform a meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of exogenous melatonin in advancing sleep-wake rhythm in patients with delayed sleep phase disorder.
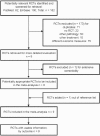
Design: Meta analysis of papers indexed for PubMed, Embase, and the abstracts of sleep and chronobiologic societies (1990-2009).
Patients: Individuals with delayed sleep phase disorder.
Interventions: Administration of melatonin.
Measurements and results: A meta-analysis of data of randomized controlled trials involving individuals with delayed sleep phase disorder that were published in English, compared melatonin with placebo, and reported 1 or more of the following: endogenous melatonin onset, clock hour of sleep onset, wake-up time, sleep-onset latency, and total sleep time. The 5 trials including 91 adults and 4 trials including 226 children showed that melatonin treatment advanced mean endogenous melatonin onset by 1.18 hours (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.89-1.48 h) and clock hour of sleep onset by 0.67 hours (95% CI: 0.45-0.89 h). Melatonin decreased sleep-onset latency by 23.27 minutes (95% CI: 4.83 -41.72 min). The wake-up time and total sleep time did not change significantly.
Conclusions: Melatonin is effective in advancing sleep-wake rhythm and endogenous melatonin rhythm in delayed sleep phase disorder.
Keywords: Melatonin; delayed sleep phase disorder; meta-analysis.
Figures

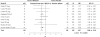
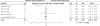

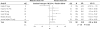
Comment in
-
Shedding light on the effectiveness of melatonin for circadian rhythm sleep disorders.Sleep. 2010 Dec;33(12):1581-2. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.12.1581. Sleep. 2010. PMID: 21120118 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pandi-Perumal SR, Smits M, Spence W, et al. Dim light melatonin onset (DLMO): a tool for the analysis of circadian phase in human sleep and chronobiological disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007;31:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Weitzman ED, Czeisler CA, Coleman RM, et al. Delayed sleep phase syndrome. A chronobiological disorder with sleep-onset insomnia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981;38:737–46. - PubMed
-
- Regestein QR, Monk TH. Delayed sleep phase syndrome: a review of its clinical aspects. Am J Psychiatry. 1995;152:602–8. - PubMed
-
- Czeisler CA, Richardson GS, Coleman RM, et al. Chronotherapy: resetting the circadian clocks of patients with delayed sleep phase insomnia. Sleep. 1981;4:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Rosenthal NE, Joseph-Vanderpool JR, Levendosky AA, et al. Phase-shifting effects of bright morning light as treatment for delayed sleep phase syndrome. Sleep. 1990;13:354–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

