Therapy-related acute leukemia in breast cancer patients: twelve cases treated with a topoisomerase inhibitor
- PMID: 21120206
- PMCID: PMC2983048
- DOI: 10.5045/kjh.2010.45.3.177
Therapy-related acute leukemia in breast cancer patients: twelve cases treated with a topoisomerase inhibitor
Abstract
Background: Therapy-related myeloid neoplasm (t-MN) is a distinct class of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the World Health Organization (WHO) classification. Both AML and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) may develop after treatment for primary cancer. Topoisomerase inhibitors are commonly used to treat breast cancer patients and are well-known for their effect on leukemogenesis of therapy-related acute leukemias (t-AL).
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated bone marrow test results, chromosomal findings, and clinical characteristics of 12 patients who received topoisomerase inhibitors for breast cancer treatment and later developed acute leukemia.
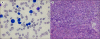
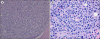
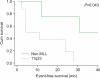
Results: Fourteen patients (0.2%) developed t-AL after treatment for breast cancer. Topoisomerase inhibitors were administered to 12 patients. Among them, 9 patients (75%, 9/12) were diagnosed with therapy-related AML (t-AML) and 3 patients (25%, 3/12) with therapy-related ALL (t-ALL). Eight patients (67%, 8/12) showed translocation involving 11q23 and 3 different partner genes, 19p13.1 (37.5%, 3/8), 9p22 (37.5%, 3/8), and 4q21 (25%, 2/8). The median interval between completion of chemotherapy for breast cancer and occurrence of t-AL was 25 months. Patients with 11q23 translocation showed markedly poorer event-free survival than the group without involvement of 11q23.
Conclusion: The incidence rate of t-AL after treatment for breast cancer was 0.2% in a tertiary hospital in Korea. Translocation involving the MLL gene was frequently found in t-AL caused by a topoisomerase inhibitor and was related to poor prognosis.
Keywords: 11q23; Breast cancer; Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia; Topoisomerase inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rearrangements of the MLL gene in therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia in patients previously treated with agents targeting DNA-topoisomerase II.Blood. 1993 Dec 15;82(12):3705-11. Blood. 1993. PMID: 8260707
-
Clinical and biological characteristics of adult de novo and secondary acute myeloid leukemia with balanced 11q23 chromosomal anomaly or MLL gene rearrangement compared to cases with unbalanced 11q23 anomaly: confirmation of the existence of different entities with 11q23 breakpoint.Leukemia. 1998 Jan;12(1):25-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400853. Leukemia. 1998. PMID: 9436917
-
Molecular analysis of 13 cases of MLL/11q23 secondary acute leukemia and identification of topoisomerase II consensus-binding sequences near the chromosomal breakpoint of a secondary leukemia with the t(4;11).Leukemia. 1995 Aug;9(8):1305-12. Leukemia. 1995. PMID: 7643617
-
Secondary leukemias induced by topoisomerase-targeted drugs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Oct 1;1400(1-3):233-55. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(98)00139-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9748598 Review.
-
Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with MLL rearrangements following DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors, an increasing problem: report on two new cases and review of the literature since 1992.Br J Haematol. 2001 Sep;114(3):539-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.03000.x. Br J Haematol. 2001. PMID: 11552977 Review.
Cited by
-
Leukemogenic rearrangements at the mixed lineage leukemia gene (MLL)-multiple rather than a single mechanism.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Jun 25;3:41. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2015.00041. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26161385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms in 39 Korean patients: a single institution experience.Ann Lab Med. 2013 Mar;33(2):97-104. doi: 10.3343/alm.2013.33.2.97. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Ann Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23483787 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of prognostic factors in patients with therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia.Blood Res. 2013 Sep;48(3):185-92. doi: 10.5045/br.2013.48.3.185. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Blood Res. 2013. PMID: 24086938 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm-unclassifiable in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia: a case report and literature review.J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211018426. doi: 10.1177/03000605211018426. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34057843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leone G, Fianchi L, Pagano L, Voso MT. Incidence and susceptibility to therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. Chem Biol Interact. 2010;184:39–45. - PubMed
-
- Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–951. - PubMed
-
- Leone G, Pagano L, Ben-Yehuda D, Voso MT. Therapy-related leukemia and myelodysplasia: susceptibility and incidence. Haematologica. 2007;92:1389–1398. - PubMed
-
- Smith RE, Bryant J, DeCillis A, Anderson S. Acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide adjuvant therapy for operable breast cancer: the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Experience. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1195–1204. - PubMed
-
- Statistics of cancer reported by national cancer information center. Seoul, Korea: national cancer information center; 2006-2007. [Accessed July 21, 2010]. at http://www.cancer.go.kr/cms/statics/incidence/index.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

