Dissociable roles of mGlu5 and dopamine receptors in the rewarding and sensitizing properties of morphine and cocaine
- PMID: 21120457
- PMCID: PMC3063544
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-010-2095-1
Dissociable roles of mGlu5 and dopamine receptors in the rewarding and sensitizing properties of morphine and cocaine
Abstract
Rationale: Drugs of abuse are initially used because of their rewarding properties. As a result of repeated drug exposure, sensitization to certain behavioral effects of drugs occurs, which may facilitate the development of addiction. Recent studies have implicated the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu5 receptor) in drug reward, but its role in sensitization is unclear. Stimulation of dopamine receptors plays an important role in drug reward, but not in the sensitizing properties of cocaine and morphine.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the role of mGlu5 and dopamine receptors in the development of cocaine- and morphine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) and psychomotor sensitization.
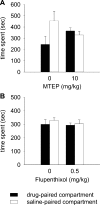
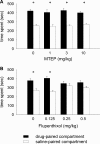
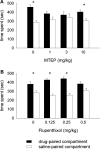
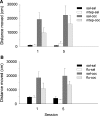
Materials and methods: Rats were treated with the mGlu5 receptor antagonist MTEP (0, 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg, i.p.) or the dopamine receptor antagonist α-flupenthixol (0, 0.125, 0.25, and 0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) during place conditioning with either morphine (3 mg/kg, s.c.) or cocaine (15 mg/kg, i.p.). Furthermore, MTEP (1 mg/kg, i.p.) or α-flupenthixol (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) was co-administered during cocaine (30 mg/kg, i.p.) or morphine (3.0 mg/kg, s.c.) pretreatment and psychomotor sensitization was tested 3 weeks post-treatment.
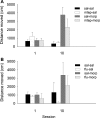
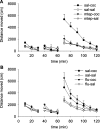
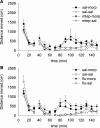
Results: MTEP attenuated the development of morphine- but not cocaine-induced CPP. In contrast, MTEP suppressed the development of cocaine- but not morphine-induced psychomotor sensitization. α-Flupenthixol blocked the development of both cocaine- and morphine-induced CPP but did not affect the development of sensitization to either drug.
Conclusion: Dopamine receptor stimulation mediates cocaine and morphine reward but not sensitization. In contrast, the role of mGlu5 receptors in reward and sensitization is drug-specific.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists on the behavioral sensitization to motor effects of cocaine in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Sep;187(4):397-404. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0440-1. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16896963
-
The mGluR5 antagonist MPEP reduces the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine but not other drugs of abuse.Synapse. 2003 Mar;47(3):240-2. doi: 10.1002/syn.10166. Synapse. 2003. PMID: 12494407
-
Effects of MPEP on locomotion, sensitization and conditioned reward induced by cocaine or morphine.Neuropharmacology. 2004 Dec;47(7):973-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.07.037. Neuropharmacology. 2004. PMID: 15555632
-
Dissociation of the effects of MTEP [3-[(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl]piperidine] on conditioned reinstatement and reinforcement: comparison between cocaine and a conventional reinforcer.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Jun;329(3):1084-90. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.151357. Epub 2009 Mar 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19258516 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 localized in the limbic forebrain is critical for the development of morphine-induced rewarding effect in mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Sep;20(6):1633-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03609.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15355330
Cited by
-
Social play behavior in adolescent rats is mediated by functional activity in medial prefrontal cortex and striatum.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Sep;38(10):1899-909. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.83. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23568326 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of neuronal dopamine D2 receptor attenuates morphine tolerance in mice spinal cord.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 22;6:38746. doi: 10.1038/srep38746. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 28004735 Free PMC article.
-
Amphetamine and cocaine suppress social play behavior in rats through distinct mechanisms.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Apr;231(8):1503-15. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3272-9. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24057815 Free PMC article.
-
mGlu receptors and drug addiction.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal. 2012 May;1(3):281-295. doi: 10.1002/wmts.18. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal. 2012. PMID: 22662312 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in brain reward deficits associated with cocaine and nicotine withdrawal and somatic signs of nicotine withdrawal.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 May;221(2):317-27. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2578-8. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22147259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acquas E, Carboni E, Leone P, Di Chiara G. SCH 23390 blocks drug-conditioned place-preference and place-aversion: anhedonia (lack of reward) or apathy (lack of motivation) after dopamine-receptor blockade? Psychopharmacology. 1989;99:151–155. - PubMed
-
- Acquas E, Di Chiara G. D1 receptor blockade stereospecifically impairs the acquisition of drug-conditioned place preference and place aversion. Behav Pharmacol. 1994;5:555–569. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JJ, Rao SP, Rowe B, Giracello DR, Holtz G, Chapman DF, Tehrani L, Bradbury MJ, Cosford ND, Varney MA. [3H]Methoxymethyl-3-[(2-methyl-1, 3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl]pyridine binding to metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 in rodent brain: in vitro and in vivo characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;303:1044–1051. - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Narita M, Shibasaki M, Suzuki T. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 localized in the limbic forebrain is critical for the development of morphine-induced rewarding effect in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:1633–1638. - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Specio SE, Khroyan TV, Neisewander JL. Effects of intraaccumbens administration of SCH-23390 on cocaine-induced locomotion and conditioned place preference. Synapse. 1998;30:181–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

