Design of experiments approach to engineer cell-secreted matrices for directing osteogenic differentiation
- PMID: 21120695
- PMCID: PMC3069311
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-010-0217-x
Design of experiments approach to engineer cell-secreted matrices for directing osteogenic differentiation
Abstract
The presentation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins provides an opportunity to instruct the phenotype and behavior of responsive cells. Decellularized cell-secreted matrix coatings (DM) represent a biomimetic culture surface that retains the complexity of the natural ECM. Microenvironmental culture conditions alter the composition of these matrices and ultimately the ability of DMs to direct cell fate. We employed a design of experiments (DOE) multivariable analysis approach to determine the effects and interactions of four variables (culture duration, cell seeding density, oxygen tension, and media supplementation) on the capacity of DMs to direct the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). DOE analysis revealed that matrices created with extended culture duration, ascorbate-2-phosphate supplementation, and in ambient oxygen tension exhibited significant correlations with enhanced hMSC differentiation. We validated the DOE model results using DMs predicted to have superior (DM1) or lesser (DM2) osteogenic potential for naïve hMSCs. Compared to cells on DM2, hMSCs cultured on DM1 expressed 2-fold higher osterix levels and deposited 3-fold more calcium over 3 weeks. Cells on DM1 coatings also exhibited greater proliferation and viability compared to DM2-coated substrates. This study demonstrates that DOE-based analysis is a powerful tool for optimizing engineered systems by identifying significant variables that have the greatest contribution to the target output.
Figures


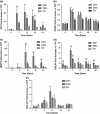
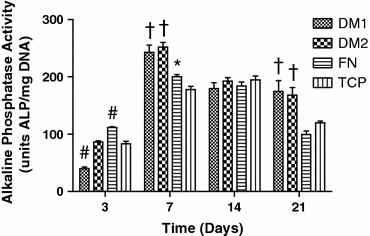
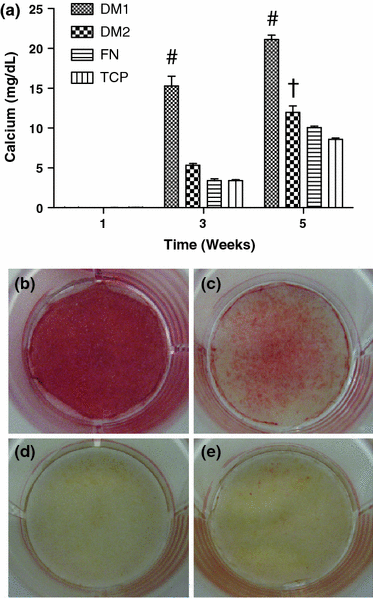
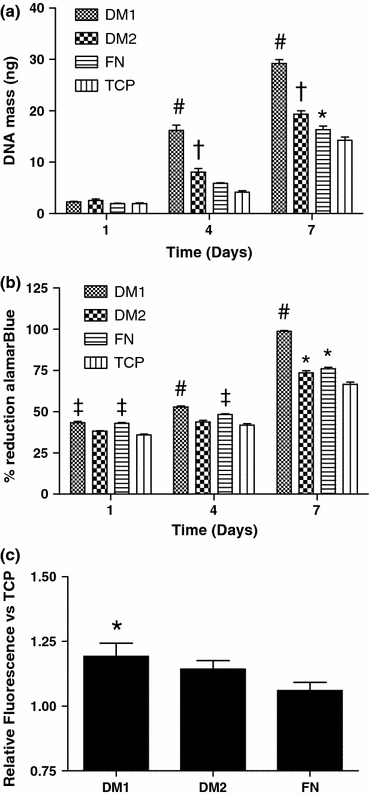

References
-
- Bancroft GN, Sikavitsas VI, van den Dolder J, Sheffield TL, Ambrose CG, Jansen JA, Mikos AG. Fluid flow increases mineralized matrix deposition in 3D perfusion culture of marrow stromal osteoblasts in a dose-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:12600–12605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202296599. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

