In-cell protein NMR and protein leakage
- PMID: 21120863
- PMCID: PMC3016450
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.22906
In-cell protein NMR and protein leakage
Abstract
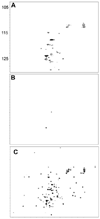
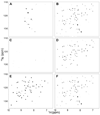
In-cell nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a tool for studying proteins under physiologically relevant conditions. In some instances, however, protein signals from leaked protein are observed in the liquid surrounding the cells. Here, we examine the expression of four proteins in Escherichia coli. We describe the controls that should be used for in-cell NMR experiments and show that leakage is likely when the protein being studied exceeds ∼20% of the total cellular protein.
© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Zimmerman SB, Trach SO. Estimation of macromolecule concentrations and excluded volume effects for the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1991;222:599–620. - PubMed
-
- Luby-Phelps K. Cytoarchitecture and physical properties of cytoplasm: Volume, viscosity, diffusion, intracellular surface area. Int Rev Cytol. 2000;192:189–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

