Boron neutron capture therapy induces apoptosis of glioma cells through Bcl-2/Bax
- PMID: 21122152
- PMCID: PMC3003659
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-661
Boron neutron capture therapy induces apoptosis of glioma cells through Bcl-2/Bax
Abstract
Background: Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is an alternative treatment modality for patients with glioma. The aim of this study was to determine whether induction of apoptosis contributes to the main therapeutic efficacy of BNCT and to compare the relative biological effect (RBE) of BNCT, γ-ray and reactor neutron irradiation.
Methods: The neutron beam was obtained from the Xi'an Pulsed Reactor (XAPR) and γ-rays were obtained from [60Co] γ source of the Fourth Military Medical University (FMMU) in China. Human glioma cells (the U87, U251, and SHG44 cell lines) were irradiated by neutron beams at the XAPR or [60Co] γ-rays at the FMMU with different protocols: Group A included control nonirradiated cells; Group B included cells treated with 4 Gy of [60Co] γ-rays; Group C included cells treated with 8 Gy of [60Co] γ-rays; Group D included cells treated with 4 Gy BPA (p-borono-phenylalanine)-BNCT; Group E included cells treated with 8 Gy BPA-BNCT; Group F included cells irradiated in the reactor for the same treatment period as used for Group D; Group G included cells irradiated in the reactor for the same treatment period as used for Group E; Group H included cells irradiated with 4 Gy in the reactor; and Group I included cells irradiated with 8 Gy in the reactor. Cell survival was determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium (MTT) cytotoxicity assay. The morphology of cells was detected by Hoechst33342 staining and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The apoptosis rate was detected by flow cytometer (FCM). The level of Bcl-2 and Bax protein was measured by western blot analysis.
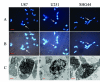
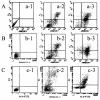
Results: Proliferation of U87, U251, and SHG44 cells was much more strongly inhibited by BPA-BNCT than by irradiation with [60Co] γ-rays (P < 0.01). Nuclear condensation was determined using both a fluorescence technique and electron microscopy in all cell lines treated with BPA-BNCT. Furthermore, the cellular apoptotic rates in Group D and Group E treated with BPA-BNCT were significantly higher than those in Group B and Group C irradiated by [60Co] γ-rays (P < 0.01). The clonogenicity of glioma cells was reduced by BPA-BNCT compared with cells treated in the reactor (Group F, G, H, I), and with the control cells (P < 0.01). Upon BPA-BNCT treatment, the Bax level increased in glioma cells, whereas Bcl-2 expression decreased.
Conclusions: Compared with γ-ray and reactor neutron irradiation, a higher RBE can be achieved upon treatment of glioma cells with BNCT. Glioma cell apoptosis induced by BNCT may be related to activation of Bax and downregulation of Bcl-2.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy for malignant glioma: a pilot neutron irradiation study using boron phenylalanine, sodium borocaptate and liposomal borocaptate with a heterotopic U87 glioblastoma model in SCID mice.Int J Radiat Biol. 2020 Jul;96(7):868-878. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1761039. Epub 2020 May 12. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020. PMID: 32339057
-
Boron neutron-capture therapy (BNCT) for glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) using the epithermal neutron beam at the Brookhaven National Laboratory.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998 Mar 1;40(4):829-34. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(97)00891-2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998. PMID: 9531367 Clinical Trial.
-
The effectiveness of the high-LET radiations from the boron neutron capture [10B(n,α) 7Li] reaction determined for induction of chromosome aberrations and apoptosis in lymphocytes of human blood samples.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2015 Mar;54(1):91-102. doi: 10.1007/s00411-014-0577-y. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25428113
-
From Nuclear Reactor-Based to Proton Accelerator-Based Therapy: The Finnish Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Experience.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2023 Apr;38(3):184-191. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2022.0059. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2023. PMID: 36269660 Review.
-
Rat brain tumor models to assess the efficacy of boron neutron capture therapy: a critical evaluation.J Neurooncol. 2003 Mar-Apr;62(1-2):61-74. doi: 10.1007/BF02699934. J Neurooncol. 2003. PMID: 12749703 Review.
Cited by
-
The Anti-Tumor Effect of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy in Glioblastoma Subcutaneous Xenograft Model Using the Proton Linear Accelerator-Based BNCT System in Korea.Life (Basel). 2022 Aug 19;12(8):1264. doi: 10.3390/life12081264. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36013445 Free PMC article.
-
'Cell knife' for cancer: the clinician's perspective.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 17;16:1536355. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1536355. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40313942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Characterization of SAS Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Relation to Both BPA and Neutron Irradiation Doses.Cells. 2023 Jun 6;12(12):1562. doi: 10.3390/cells12121562. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371031 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis through Bcl-2/Bax and cleaved caspase up-regulation in melanoma treated by boron neutron capture therapy.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059639. Epub 2013 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527236 Free PMC article.
-
LRIG1 enhances chemosensitivity by modulating BCL-2 expression and receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in glioma cells.Yonsei Med J. 2014 Sep;55(5):1196-205. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.5.1196. Yonsei Med J. 2014. PMID: 25048475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang W, Barth RF, Wu G, Huo T, Tjarks W, Ciesielski M, Fenstermaker RA, Ross BD, Wikstrand CJ, Riley KJ, Binns PJ. Convection enhanced delivery of boronated EGF as a molecular targeting agent for neutron capture therapy of brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 2009;95:355–365. doi: 10.1007/s11060-009-9945-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang W, Barth RF, Wu G, Bandyopadhyaya AK, Thirumamagal BT, Tjarks W, Binns PJ, Riley K, Patel H, Coderre JA, Ciesielski MJ, Fenstermaker RA. Boronated epidermal growth factor as a delivery agent for neutron capture therapy of EGF receptor positive gliomas. Appl Radiat Isot. 2004;61:981–985. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2004.05.071. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barth RF, Yang W, Coderre JA. Rat brain tumor models to assess the efficacy of boron neutron capture therapy: a critical evaluation. J Neurooncol. 2003;62:61–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

