Galectin-1 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation and its re-expression induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 21122983
- PMCID: PMC3023883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.027
Galectin-1 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation and its re-expression induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
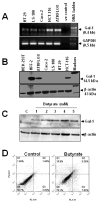
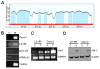
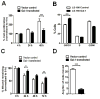
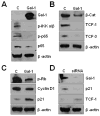
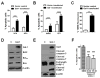
Galectin-1 (gal-1) is an important molecule secreted by many tumors, which induces apoptosis in activated T-cells and promotes tumor angiogenesis, both of which phenomena facilitate successful establishment of tumor in the body. However, little is known about the function of intracellular gal-1 or its transcriptional regulation in colorectal cancer (CRC). Here, we demonstrate that gal-1 expression is epigenetically regulated in CRC through promoter hypermethylation. Intracellular gal-1 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in CRC cells with concomitant down-regulation of Wnt and NF-κB signaling pathways. Together, these data suggested that gal-1 silencing imparts CRC with the ability to proliferate and escape apoptosis.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures

References
-
- Rustgi AK. Molecular genetics and colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:1223–5. - PubMed
-
- Issa JP. The epigenetics of colorectal cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;910:140–53. discussion 153–5. - PubMed
-
- Shen L, Issa JP. Epigenetics in colorectal cancer. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2002;18:68–73. - PubMed
-
- Liu FT, Rabinovich GA. Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:29–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

