Surfactant protein A (SP-A)-mediated clearance of Staphylococcus aureus involves binding of SP-A to the staphylococcal adhesin eap and the macrophage receptors SP-A receptor 210 and scavenger receptor class A
- PMID: 21123169
- PMCID: PMC3039347
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125567
Surfactant protein A (SP-A)-mediated clearance of Staphylococcus aureus involves binding of SP-A to the staphylococcal adhesin eap and the macrophage receptors SP-A receptor 210 and scavenger receptor class A
Abstract
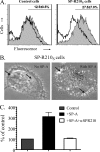
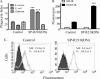
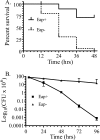
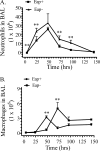
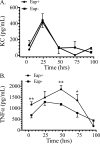
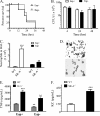
Staphylococcus aureus causes life-threatening pneumonia in hospitals and deadly superinfection during viral influenza. The current study investigated the role of surfactant protein A (SP-A) in opsonization and clearance of S. aureus. Previous studies showed that SP-A mediates phagocytosis via the SP-A receptor 210 (SP-R210). Here, we show that SP-R210 mediates binding and control of SP-A-opsonized S. aureus by macrophages. We determined that SP-A binds S. aureus through the extracellular adhesin Eap. Consequently, SP-A enhanced macrophage uptake of Eap-expressing (Eap(+)) but not Eap-deficient (Eap(-)) S. aureus. In a reciprocal fashion, SP-A failed to enhance uptake of Eap(+) S. aureus in peritoneal Raw264.7 macrophages with a dominant negative mutation (SP-R210(DN)) blocking surface expression of SP-R210. Accordingly, WT mice cleared infection with Eap(+) but succumbed to sublethal infection with Eap- S. aureus. However, SP-R210(DN) cells compensated by increasing non-opsonic phagocytosis of Eap(+) S. aureus via the scavenger receptor scavenger receptor class A (SR-A), while non-opsonic uptake of Eap(-) S. aureus was impaired. Macrophages express two isoforms: SP-R210(L) and SP-R210(S). The results show that WT alveolar macrophages are distinguished by expression of SP-R210(L), whereas SR-A(-/-) alveolar macrophages are deficient in SP-R210(L) expressing only SP-R210(S). Accordingly, SR-A(-/-) mice were highly susceptible to both Eap(+) and Eap(-) S. aureus. The lungs of susceptible mice generated abnormal inflammatory responses that were associated with impaired killing and persistence of S. aureus infection in the lung. In conclusion, alveolar macrophage SP-R210(L) mediates recognition and killing of SP-A-opsonized S. aureus in vivo, coordinating inflammatory responses and resolution of S. aureus pneumonia through interaction with SR-A.
Figures


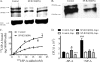
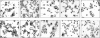
Similar articles
-
Surfactant protein A mediates pulmonary clearance of Staphylococcus aureus.Respir Res. 2014 Aug 5;15(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0085-2. Respir Res. 2014. PMID: 25091948 Free PMC article.
-
SP-R210 (Myo18A) Isoforms as Intrinsic Modulators of Macrophage Priming and Activation.PLoS One. 2015 May 12;10(5):e0126576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126576. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25965346 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary surfactant protein A augments the phagocytosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae by alveolar macrophages through a casein kinase 2-dependent increase of cell surface localization of scavenger receptor A.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 14;279(20):21421-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312490200. Epub 2004 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14993215
-
Immunoregulatory function of SP-A.Mol Immunol. 2024 Feb;166:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2024.01.005. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38244369 Review.
-
Pulmonary collectins in innate immunity of the lung.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Aug;9(8):1871-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00953.x. Epub 2007 May 8. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17490408 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa express and secrete human surfactant proteins.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053705. Epub 2013 Jan 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349731 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Lipoproteins Are Critical for Pulmonary Innate Defense against Staphylococcus aureus Quorum Sensing.J Immunol. 2016 Jan 1;196(1):328-35. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501835. Epub 2015 Nov 25. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26608923 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus proteases degrade lung surfactant protein A potentially impairing innate immunity of the lung.J Innate Immun. 2013;5(3):251-60. doi: 10.1159/000345417. Epub 2012 Dec 11. J Innate Immun. 2013. PMID: 23235402 Free PMC article.
-
Host Defense and the Airway Epithelium: Frontline Responses That Protect against Bacterial Invasion and Pneumonia.J Pathog. 2011;2011:249802. doi: 10.4061/2011/249802. Epub 2011 Sep 22. J Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22567325 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of surfactant protein A in bacterial sinusitis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017 Sep;7(9):897-903. doi: 10.1002/alr.21985. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017. PMID: 28727907 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

