Interleukin-27 and interferon-gamma are involved in regulation of autoimmune arthritis
- PMID: 21123181
- PMCID: PMC3024777
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187013
Interleukin-27 and interferon-gamma are involved in regulation of autoimmune arthritis
Abstract
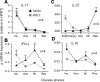
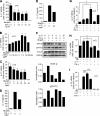
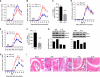
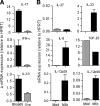
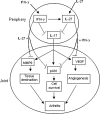
Inflammation underlying immune pathology and tissue damage involves an intricate interplay between multiple immunological and biochemical mediators. Cytokines represent the key immune mediators that trigger a cascade of reactions that drive processes such as angiogenesis and proteolytic damage to tissues. IL-17 has now been shown to be a pivotal cytokine in many autoimmune diseases, supplanting the traditional Th1-Th2 paradigm. Also, the dual role of proinflammatory IFN-γ has unraveled new complexities in the cytokine biology of such disorders. A major hurdle in fully understanding the effector pathways in these disorders is the lack of information regarding the temporal kinetics of the cytokines during the course of the disease, as well as the interplay among the key cytokines. Using an experimental model of arthritic inflammation, we demonstrate that the temporal expression of cytokines during the incubation phase is a critical determinant of disease susceptibility. The susceptible rats raised a vigorous IL-17 response early, followed by IFN-γ and IL-27 response in that sequence, whereas the resistant rats displayed an early and concurrent response to these three cytokines. Accordingly, treatment with exogenous IFN-γ/IL-27 successfully controlled arthritic inflammation and inhibited the defined mediators of inflammation, angiogenesis, cell survival, apoptosis, and tissue damage. Furthermore, IFN-γ enhanced IL-27 secretion, revealing a cooperative interplay between the two cytokines. Our results offer a novel immunobiochemical perspective on the pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis and its therapeutic control.
Figures
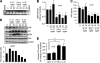
Similar articles
-
Regulation of autoimmune arthritis by the pro-inflammatory cytokine interferon-gamma.Clin Immunol. 2008 Apr;127(1):98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2008.01.003. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18276192 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Th17/Treg balance and dysregulated IL-1β response influence susceptibility/resistance to experimental autoimmune arthritis.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;28(3):318-28. doi: 10.1177/0394632015595757. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26227656 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous IL-22 plays a dual role in arthritis: regulation of established arthritis via IFN-γ responses.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 27;9(3):e93279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093279. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24676270 Free PMC article.
-
How interferon-gamma keeps autoimmune diseases in check.Trends Immunol. 2008 Oct;29(10):479-86. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.07.002. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Trends Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18775671 Review.
-
A cytokine-centric view of the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune arthritis.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Dec;31(12):927-40. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0094. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 22149412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetics and interplay of mediators of inflammation-induced bone damage in the course of adjuvant arthritis.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013 Jan-Mar;26(1):37-48. doi: 10.1177/039463201302600104. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23527707 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Th17 immunity in chronic ocular surface disorders.Ocul Surf. 2021 Jan;19:157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2020.05.009. Epub 2020 May 26. Ocul Surf. 2021. PMID: 32470612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New directions in the basic and translational biology of interleukin-27.Trends Immunol. 2012 Feb;33(2):91-7. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.11.003. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Trends Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22177689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Prednisone-Based Arthritis Therapy with Targeted IL-27 Gene Delivery.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Jun 9;9(6):248. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9060248. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35735491 Free PMC article.
-
Modified huo-luo-xiao-ling dan suppresses adjuvant arthritis by inhibiting chemokines and matrix-degrading enzymes.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:589256. doi: 10.1155/2012/589256. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22474510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Firestein G. S. (2003) Nature 423, 356–361 - PubMed
-
- Newton J. L., Harney S. M., Wordsworth B. P., Brown M. A. (2004) Genes Immun. 5, 151–157 - PubMed
-
- de Carvalho J. F., Pereira R. M., Shoenfeld Y. (2009) Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed) 1, 501–509 - PubMed
-
- Prabhakar B. S., Bahn R. S., Smith T. J. (2003) Endocr. Rev. 24, 802–835 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

