maxAlike: maximum likelihood-based sequence reconstruction with application to improved primer design for unknown sequences
- PMID: 21123221
- PMCID: PMC3031029
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq651
maxAlike: maximum likelihood-based sequence reconstruction with application to improved primer design for unknown sequences
Abstract
Motivation: The task of reconstructing a genomic sequence from a particular species is gaining more and more importance in the light of the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing technologies and their limitations. Applications include not only compensation for missing data in unsequenced genomic regions and the design of oligonucleotide primers for target genes in species with lacking sequence information but also the preparation of customized queries for homology searches.
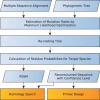
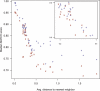
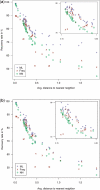
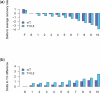
Results: We introduce the maxAlike algorithm, which reconstructs a genomic sequence for a specific taxon based on sequence homologs in other species. The input is a multiple sequence alignment and a phylogenetic tree that also contains the target species. For this target species, the algorithm computes nucleotide probabilities at each sequence position. Consensus sequences are then reconstructed based on a certain confidence level. For 37 out of 44 target species in a test dataset, we obtain a significant increase of the reconstruction accuracy compared to both the consensus sequence from the alignment and the sequence of the nearest phylogenetic neighbor. When considering only nucleotides above a confidence limit, maxAlike is significantly better (up to 10%) in all 44 species. The improved sequence reconstruction also leads to an increase of the quality of PCR primer design for yet unsequenced genes: the differences between the expected T(m) and real T(m) of the primer-template duplex can be reduced by ~26% compared with other reconstruction approaches. We also show that the prediction accuracy is robust to common distortions of the input trees. The prediction accuracy drops by only 1% on average across all species for 77% of trees derived from random genomic loci in a test dataset.
Availability: maxAlike is available for download and web server at: http://rth.dk/resources/maxAlike.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BatchPrimer3: a high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 May 29;9:253. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-253. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18510760 Free PMC article.
-
Primaclade--a flexible tool to find conserved PCR primers across multiple species.Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 1;21(7):1263-4. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti134. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15539448
-
PUNS: transcriptomic- and genomic-in silico PCR for enhanced primer design.Bioinformatics. 2004 Oct 12;20(15):2399-400. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth257. Epub 2004 Apr 8. Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15073008
-
Graphical design of primers with PerlPrimer.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;402:403-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-528-2_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17951808 Review.
-
Degenerate primer design: theoretical analysis and the HYDEN program.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;402:221-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-528-2_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17951798 Review.
Cited by
-
phoD Alkaline Phosphatase Gene Diversity in Soil.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Oct;81(20):7281-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01823-15. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26253682 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and Phylogeny of MicroRNAs - Protocols, Pitfalls, and Problems.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2257:211-233. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1170-8_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34432281
-
One origin for metallo-β-lactamase activity, or two? An investigation assessing a diverse set of reconstructed ancestral sequences based on a sample of phylogenetic trees.J Mol Evol. 2014 Oct;79(3-4):117-29. doi: 10.1007/s00239-014-9639-7. Epub 2014 Sep 4. J Mol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25185655 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative RNA Genomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2802:347-393. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3838-5_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38819565
-
FastML: a web server for probabilistic reconstruction of ancestral sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(Web Server issue):W580-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks498. Epub 2012 May 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22661579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browser UG. The ucsc 44 way alignments. 2010 Available at http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTrackUi?db=hg18&g=cons44way.
-
- Cha RS, Thilly WG. Specificity, efficiency, and fidelity of PCR. PCR Methods Appl. 1993;3:S18–S29. - PubMed
-
- Díaz-Uriarte R, Garland T. Effects of branch length errors on the performance of phylogenetically independent contrasts. Syst. Biol. 1998;47:654–672. - PubMed

