Editorial: 25-Hydroxycholesterol: a new life in immunology
- PMID: 21123296
- PMCID: PMC2996897
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0710418
Editorial: 25-Hydroxycholesterol: a new life in immunology
Abstract
A discussion on paper by Park and Scott revealing the signaling pathways leading to the synthesis of a potent immunoregulatory oxysterol by macrophage and dendritic cells.
Figures
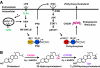
Comment on
-
Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase production by dendritic cells and macrophages is regulated by type I interferons.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Dec;88(6):1081-7. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0610318. Epub 2010 Aug 10. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20699362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lund E. G., Kerr T. A., Sakai J., Li W-P., Russell D. W. (1998) cDNA cloning of mouse and human cholesterol 25-hydroxylases, polytopic membrane proteins that synthesize a potent oxysterol regulator of lipid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 34316–34348 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

