Elements between the IgH variable (V) and diversity (D) clusters influence antisense transcription and lineage-specific V(D)J recombination
- PMID: 21123744
- PMCID: PMC3009784
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1015954107
Elements between the IgH variable (V) and diversity (D) clusters influence antisense transcription and lineage-specific V(D)J recombination
Abstract
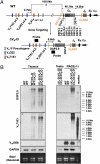
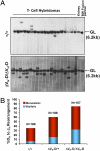
Ig and T-cell receptor (TCR) variable-region gene exons are assembled from component variable (V), diversity (D) and joining (J) gene segments during early B and T cell development. The RAG1/2 endonuclease initiates V(D)J recombination by introducing DNA double-strand breaks at borders of the germ-line segments. In mice, the Ig heavy-chain (IgH) locus contains, from 5' to 3', several hundred V(H) gene segments, 13 D segments, and 4 J(H) segments within a several megabase region. In developing B cells, IgH variable-region exon assembly is ordered with D to J(H) rearrangement occurring on both alleles before appendage of a V(H) segment. Also, IgH V(H) to DJ(H) rearrangement does not occur in T cells, even though DJ(H) rearrangements occur at low levels. In these contexts, V(D)J recombination is controlled by modulating substrate gene segment accessibility to RAG1/2 activity. To elucidate control elements, we deleted the 100-kb intergenic region that separates the V(H) and D clusters (generating ΔV(H)-D alleles). In both B and T cells, ΔV(H)-D alleles initiated high-level antisense and, at lower levels, sense transcription from within the downstream D cluster, with antisense transcripts extending into proximal V(H) segments. In developing T lymphocytes, activated germ-line antisense transcription was accompanied by markedly increased IgH D-to-J(H) rearrangement and substantial V(H) to DJ(H) rearrangement of proximal IgH V(H) segments. Thus, the V(H)-D intergenic region, and likely elements within it, can influence silencing of sense and antisense germ-line transcription from the IgH D cluster and thereby influence targeting of V(D)J recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Schatz DG. V(D)J recombination. Immunol Rev. 2004;200:5–11. - PubMed
-
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541–570. - PubMed
-
- Yancopoulos GD, Blackwell TK, Suh H, Hood L, Alt FW. Introduced T cell receptor variable region gene segments recombine in pre-B cells: Evidence that B and T cells use a common recombinase. Cell. 1986;44:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Schatz DG, Baltimore D. Uncovering the V(D)J recombinase. Cell. 2004;116:S103–S106. - PubMed
-
- Fugmann SD, Lee AI, Shockett PE, Villey IJ, Schatz DG. The RAG proteins and V(D)J recombination: Complexes, ends, and transposition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:495–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

