Structural biology: An alphavirus puzzle solved
- PMID: 21124448
- PMCID: PMC3088109
- DOI: 10.1038/468645a
Structural biology: An alphavirus puzzle solved
Abstract
Alphaviruses infect their host by binding cellular receptors and fusing with cell membranes. New structures define the receptor-binding protein of these viruses and its regulation of the membrane-fusion reaction.
Figures
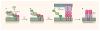
Comment on
-
Structural changes of envelope proteins during alphavirus fusion.Nature. 2010 Dec 2;468(7324):705-8. doi: 10.1038/nature09546. Nature. 2010. PMID: 21124457 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoprotein organization of Chikungunya virus particles revealed by X-ray crystallography.Nature. 2010 Dec 2;468(7324):709-12. doi: 10.1038/nature09555. Nature. 2010. PMID: 21124458
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

