Transgenic miR132 alters neuronal spine density and impairs novel object recognition memory
- PMID: 21124738
- PMCID: PMC2993964
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015497
Transgenic miR132 alters neuronal spine density and impairs novel object recognition memory
Abstract
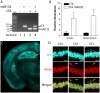
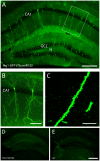
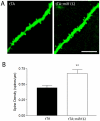
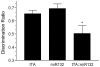
Inducible gene expression plays a central role in neuronal plasticity, learning, and memory, and dysfunction of the underlying molecular events can lead to severe neuronal disorders. In addition to coding transcripts (mRNAs), non-coding microRNAs (miRNAs) appear to play a role in these processes. For instance, the CREB-regulated miRNA miR132 has been shown to affect neuronal structure in an activity-dependent manner, yet the details of its physiological effects and the behavioral consequences in vivo remain unclear. To examine these questions, we employed a transgenic mouse strain that expresses miR132 in forebrain neurons. Morphometric analysis of hippocampal neurons revealed that transgenic miR132 triggers a marked increase in dendritic spine density. Additionally, miR132 transgenic mice exhibited a decrease in the expression of MeCP2, a protein implicated in Rett Syndrome and other disorders of mental retardation. Consistent with these findings, miR132 transgenic mice displayed significant deficits in novel object recognition. Together, these data support a role for miR132 as a regulator of neuronal structure and function, and raise the possibility that dysregulation of miR132 could contribute to an array of cognitive disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75:855–862. - PubMed
-
- Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, et al. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr. 2002;Biol12:735–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

