Alzheimer's disease: diagnostics, prognostics and the road to prevention
- PMID: 21124753
- PMCID: PMC2987528
- DOI: 10.1007/s13167-010-0024-3
Alzheimer's disease: diagnostics, prognostics and the road to prevention
Abstract
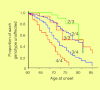
Alzheimer's disease (AD) presents one of the leading healthcare challenges of the 21st century, with a projected worldwide prevalence of >107 million cases by 2025. While biomarkers have been identified, which may correlate with disease progression or subtype for the purpose of disease monitoring or differential diagnosis, a biomarker for reliable prediction of late onset disease risk has not been available until now. This deficiency in reliable predictive biomarkers, coupled with the devastating nature of the disease, places AD at a high priority for focus by predictive, preventive and personalized medicine. Recent data, discovered using phylogenetic analysis, suggest that a variable length poly-T sequence polymorphism in the TOMM40 gene, adjacent to the APOE gene, is predictive of risk of AD age-of-onset when coupled with a subject's current age. This finding offers hope for reliable assignment of disease risk within a 5-7 year window, and is expected to guide enrichment of clinical trials in order to speed development of preventative medicines.
Figures

References
-
- ACCE model process for evaluating genetic tests. 2009. (Accessed at http://www.cdc.gov/genomics/gtesting/ACCE/index.htm.)
-
- FDA. Drug-diagnostic co-development concept paper (draft). In; 2005.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

