Using sequence-specific chemical and structural properties of DNA to predict transcription factor binding sites
- PMID: 21124945
- PMCID: PMC2987836
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001007
Using sequence-specific chemical and structural properties of DNA to predict transcription factor binding sites
Abstract
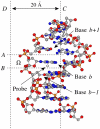
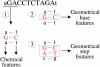
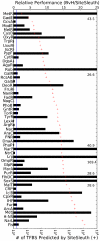
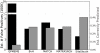
An important step in understanding gene regulation is to identify the DNA binding sites recognized by each transcription factor (TF). Conventional approaches to prediction of TF binding sites involve the definition of consensus sequences or position-specific weight matrices and rely on statistical analysis of DNA sequences of known binding sites. Here, we present a method called SiteSleuth in which DNA structure prediction, computational chemistry, and machine learning are applied to develop models for TF binding sites. In this approach, binary classifiers are trained to discriminate between true and false binding sites based on the sequence-specific chemical and structural features of DNA. These features are determined via molecular dynamics calculations in which we consider each base in different local neighborhoods. For each of 54 TFs in Escherichia coli, for which at least five DNA binding sites are documented in RegulonDB, the TF binding sites and portions of the non-coding genome sequence are mapped to feature vectors and used in training. According to cross-validation analysis and a comparison of computational predictions against ChIP-chip data available for the TF Fis, SiteSleuth outperforms three conventional approaches: Match, MATRIX SEARCH, and the method of Berg and von Hippel. SiteSleuth also outperforms QPMEME, a method similar to SiteSleuth in that it involves a learning algorithm. The main advantage of SiteSleuth is a lower false positive rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Wall ME, Hlavacek WS, Savageau MA. Design Principles for Regulator Gene Expression in a Repressible Gene Circuit. J Mol Biol. 2003;332:861–876. - PubMed
-
- Lee SK, Keasling JD. Practical pathway engineering - demonstration in integrating tools. In: Smolke CD, editor. The Metabolic Pathway Engineering Handbook: Tools and Applications. Baca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2010. pp. 12-11–12-14.
-
- Berg O, von Hippel P. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. Statistical-mechanical theory and application to operators and promoters. J Mol Biol. 1987;193:723–750. - PubMed
-
- Cartharius K, Frech K, Grote K, Klocke B, Haltmeier M, et al. MatInspector and beyond: promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2933–2942. - PubMed
-
- Chen QK, Hertz GZ, Stormo GD. MATRIX SEARCH 1.0: a computer program that scans DNA sequences for transcriptional elements using a database of weight matrices. Comput Appl Biosci. 1995;11:563–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

