Effects of the TLR2 agonists MALP-2 and Pam3Cys in isolated mouse lungs
- PMID: 21124967
- PMCID: PMC2987752
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013889
Effects of the TLR2 agonists MALP-2 and Pam3Cys in isolated mouse lungs
Abstract
Background: Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria are main causes of pneumonia or acute lung injury. They are recognized by the innate immune system via toll-like receptor-2 (TLR2) or TLR4, respectively. Among all organs, the lungs have the highest expression of TLR2 receptors, but little is known about the pulmonary consequences of their activation. Here we studied the effects of the TLR2/6 agonist MALP-2, the TLR2/1 agonist Pam(3)Cys and the TLR4 agonist lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on pro-inflammatory responses in isolated lungs.
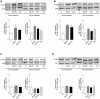
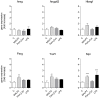
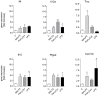
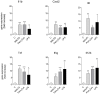
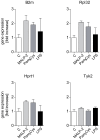
Methodology/principal findings: Isolated perfused mouse lungs were perfused for 60 min or 180 min with MALP-2 (25 ng/mL), Pam(3)Cys (160 ng/mL) or LPS (1 µg/mL). We studied mediator release by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the activation of mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and AKT/protein kinase B by immunoblotting, and gene induction by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. All agonists activated the MAPK ERK1/2 and p38, but neither JNK or AKT kinase. The TLR ligands upregulated the inflammation related genes Tnf, Il1β, Il6, Il10, Il12, Ifng, Cxcl2 (MIP-2α) and Ptgs2. MALP-2 was more potent than Pam(3)Cys in inducing Slpi, Cxcl10 (IP10) and Parg. Remarkable was the strong induction of Tnc by MALP2, which was not seen with Pam(3)Cys or LPS. The growth factor related genes Areg and Hbegf were not affected. In addition, all three TLR agonists stimulated the release of IL-6, TNF, CXCL2 and CXCL10 protein from the lungs.
Conclusions/significance: TLR2 and TLR4 activation leads to similar reactions in the lungs regarding MAPK activation, gene induction and mediator release. Several genes studied here have not yet been appreciated as targets of TLR2-activation in the lungs before, i.e., Slpi, tenascin C, Parg and Traf1. In addition, the MALP-2 dependent induction of Tnc may indicate the existence of TLR2/6-specific pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:987–995. - PubMed
-
- Zähringer U, Lindner B, Inamura S, Heine H, Alexander C. TLR2 - promiscuous or specific? A critical re-evaluation of a receptor expressing apparent broad specificity. Immunobiology. 2008;213:205–224. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura M, Naito S. Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human toll-like receptors and related genes. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005;28:886–892. - PubMed
-
- Reiling N, Hölscher C, Fehrenbach A, Kröger S, Kirschning CJ, et al. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor (TLR)2- and TLR4-mediated pathogen recognition in resistance to airborne infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 2002;169:3480–3484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

