Photounbinding of calmodulin from a family of CaM binding peptides
- PMID: 21124984
- PMCID: PMC2987815
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014050
Photounbinding of calmodulin from a family of CaM binding peptides
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have shown that fluorescently labeled antibodies can be dissociated from their antigen by illumination with laser light. The mechanism responsible for the photounbinding effect, however, remains elusive. Here, we give important insights into the mechanism of photounbinding and show that the effect is not restricted to antibody/antigen binding.
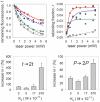
Methodology/principal findings: We present studies of the photounbinding of labeled calmodulin (CaM) from a set of CaM-binding peptides with different affinities to CaM after one- and two-photon excitation. We found that the photounbinding effect becomes stronger with increasing binding affinity. Our observation that photounbinding can be influenced by using free radical scavengers, that it does not occur with either unlabeled protein or non-fluorescent quencher dyes, and that it becomes evident shortly after or with photobleaching suggest that photounbinding and photobleaching are closely linked.
Conclusions/significance: The experimental results exclude surface effects, or heating by laser irradiation as potential causes of photounbinding. Our data suggest that free radicals formed through photobleaching may cause a conformational change of the CaM which lowers their binding affinity with the peptide or its respective binding partner.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Bingaman S, Huxley VH, Rolando ER. Fluorescent Dyes Modify Properties of Proteins Used in Microvascular Research. Microcirculation. 2003;10(2):221–231. - PubMed
-
- Luschtinetz F, Dosche C, Kumke MU. Influence of Streptavidin on the Absorption and Fluorescence Properties of Cyanine Dyes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2009;20(3):576–582. - PubMed
-
- Hoebe RA, Van Der Voort HTM, Stap J, Van Noorden CJF, Manders EMM. Qantitative Determination of the Reduction of Phototoxicity and Photobleaching by Controlled Light Exposure Microscopy. J Microsc. 2008;231(Pt 1):9–20. - PubMed
-
- Remington SJ. Fluorescent Proteins: Maturation, Photochemistry and Photophysics. Curr. Opinion in Struct Biol. 2006;16:714–721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

