Quantitative iTRAQ-Based Proteomic Identification of Candidate Biomarkers for Diabetic Nephropathy in Plasma of Type 1 Diabetic Patients
- PMID: 21124997
- PMCID: PMC2970822
- DOI: 10.1007/s12014-010-9053-0
Quantitative iTRAQ-Based Proteomic Identification of Candidate Biomarkers for Diabetic Nephropathy in Plasma of Type 1 Diabetic Patients
Abstract
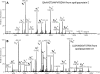
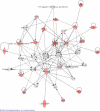
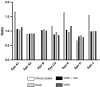
INTRODUCTION: As part of a clinical proteomics programme focused on diabetes and its complications, it was our goal to investigate the proteome of plasma in order to find improved candidate biomarkers to predict diabetic nephropathy. METHODS: Proteins derived from plasma from a cross-sectional cohort of 123 type 1 diabetic patients previously diagnosed as normoalbuminuric, microalbuminuric or macroalbuminuric were enriched with hexapeptide library beads and subsequently pooled within three groups. Proteins from the three groups were compared by online liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry in three identical repetitions using isobaric mass tags (iTRAQ). The results were further analysed with ingenuity pathway analysis. Levels of apolipoprotein A1, A2, B, C3, E and J were analysed and validated by a multiplex immunoassay in 20 type 1 diabetic patients with macroalbuminuria and 10 with normoalbuminuria. RESULTS: A total of 112 proteins were identified in at least two out of three replicates. The global protein ratios were further evaluated by ingenuity pathway analysis, resulting in the recognition of apolipoprotein A2, B, C3, D and E as key nodes in the top-rated network. The multiplex immunoassay confirmed the overall protein expression patterns observed by the iTRAQ analysis. CONCLUSION: The candidate biomarkers discovered in this cross-sectional cohort may turn out to be progression biomarkers and might have several clinical applications in the treatment and monitoring of diabetic nephropathy; however, they need to be confirmed in a longitudinal cohort. ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s12014-010-9053-0) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma proteome analysis of patients with type 1 diabetes with diabetic nephropathy.Proteome Sci. 2010 Feb 3;8:4. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-8-4. Proteome Sci. 2010. PMID: 20205888 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of early-stage biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease using ms-based metabolomics (FinnDiane study).Metabolomics. 2012 Feb;8(1):109-119. doi: 10.1007/s11306-011-0291-6. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Metabolomics. 2012. PMID: 22279428 Free PMC article.
-
iTRAQ plasma proteomics analysis for candidate biomarkers of type 2 incipient diabetic nephropathy.Clin Proteomics. 2019 Jul 31;16:33. doi: 10.1186/s12014-019-9253-1. eCollection 2019. Clin Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31384238 Free PMC article.
-
Shotgun proteomics using the iTRAQ isobaric tags.Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2006 Jun;5(2):112-20. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ell018. Epub 2006 May 10. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2006. PMID: 16772272 Review.
-
Quantitative proteomics analysis to identify diffuse axonal injury biomarkers in rats using iTRAQ coupled LC-MS/MS.J Proteomics. 2016 Feb 5;133:93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2015.12.014. Epub 2015 Dec 19. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26710722 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Pathways of Diabetic Kidney Disease Inferred from Proteomics.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Jan 12;16:117-128. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S392888. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 36760602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics for prediction of disease progression and response to therapy in diabetic kidney disease.Diabetologia. 2016 Sep;59(9):1819-31. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4001-9. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27344310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrated approach based on multiplexed protein array and iTRAQ labeling for in-depth identification of pathways associated to IVF outcome.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 16;8(10):e77303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077303. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24146976 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Mucosal Proteins and Bacteriome Are Shaped by the Saturation Index of Dietary Lipids.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 16;11(2):418. doi: 10.3390/nu11020418. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30781503 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics and systems biology for understanding diabetic nephropathy.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012 Aug;5(4):479-90. doi: 10.1007/s12265-012-9372-9. Epub 2012 May 12. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22581264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Finne P, Reunanen A, Stenman S, Groop P-H, Gronhagen-Riska C. Incidence of end-stage renal disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. JAMA. 2005;294:1782–87. - PubMed
-
- Daneman D. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 2006;367:847–58. - PubMed
-
- Cameron JS. The discovery of diabetic nephropathy: from small print to centre stage. J Nephrol. 2006;19:75–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
