Adventitia-derived hydrogen peroxide impairs relaxation of the rat carotid artery via smooth muscle cell p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 21126185
- PMCID: PMC3151421
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3631
Adventitia-derived hydrogen peroxide impairs relaxation of the rat carotid artery via smooth muscle cell p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
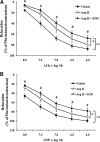
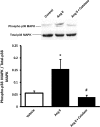
The role of adventitia-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) in vascular disease and impaired vascular relaxation is not clear. Based on robust adventitial ROS generation and effects on MAPK involvement in vascular dysfunction, we hypothesized that adventitia-derived ROS hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) impairs vascular relaxation through activation of medial smooth muscle p38 MAPK. By using a novel in vivo model, the adventitial surface of rat carotid arteries was bathed in situ for 90 min with vehicle, angiotensin II (AngII; 500 nM), AngII+H(2)O(2)-scavenger catalase (3,000 U/ml), AngII+p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (10 μM), or AngII+superoxide dismutase (SOD; 150 U/ml). After these in vivo treatments, ex vivo tone measurements on isolated vessels revealed that periadventitial application of AngII impaired both acetylcholine-induced (endothelium-dependent) and sodium nitroprusside-induced (endothelium-independent) relaxations. In vivo coincubation with catalase or SB203580 significantly improved, but SOD exacerbated AngII-induced impairment of in vitro endothelium-dependent and -independent vascular relaxations. Western blots of vascular media, separated from the adventitia, demonstrated increased medial p38 MAPK activation and decreased medial phosphatase SHP-2 activity in AngII-treated vessels. These effects were reversed by in vivo periadventitial addition of catalase. These findings provide the first evidence that adventitia-derived H(2)O(2) participates in vascular dysfunction through p38 MAPK activation and SHP-2 inhibition.
Figures




References
-
- Ardanaz N. Beierwaltes WH. Pagano PJ. Comparison of H2O2-induced vasoconstriction in the abdominal aorta and mesenteric artery of the mouse. Vascul Pharmacol. 2007;47:288–294. - PubMed
-
- Ardanaz N. Beierwaltes WH. Pagano PJ. Distinct hydrogen peroxide-induced constriction in multiple mouse arteries: potential influence of vascular polarization. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Ardanaz N. Pagano PJ. Hydrogen peroxide as a paracrine vascular mediator: regulation and signaling leading to dysfunction. Exp Biol Med. 2006;231:237–251. - PubMed
-
- Azuma Y. Kosaka K. Kashimata M. Phospholipase D-dependent and -independent p38MAPK activation pathways are required for superoxide production and chemotactic induction, respectively, in rat neutrophils stimulated by fMLP. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;568:260–268. - PubMed
-
- Azumi H. Inoue N. Takeshita S. Rikitake Y. Kawashima S. Hayashi Y. Itoh H. Yokoyama M. Expression of NADH/NADPH oxidase p22phox in human coronary arteries. Circulation. 1999;100:1494–1498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

