Redox signaling and the innate immune system in alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 21126203
- PMCID: PMC3118704
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3746
Redox signaling and the innate immune system in alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
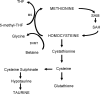
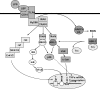
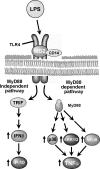
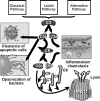
The development of alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a complex process involving both parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells resident in the liver. Although the mechanisms for ALD are not completely understood, it is clear that increased oxidative stress, and activation of the innate immune system are essential elements in the pathophysiology of ALD. Oxidative stress from ethanol exposure results from increased generation of reactive oxygen species and decreased hepatocellular antioxidant activity, including changes in the thioredoxin/peroxiredoxin family of proteins. Both cellular and circulating components of the innate immune system are activated by exposure to ethanol. For example, ethanol exposure enhances toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4)-dependent cytokine expression by Kupffer cells, likely due, at least in part, to dysregulation of redox signaling. Similarly, complement activation in response to ethanol leads to increased production of the anaphylatoxins, C3a and C5a, and activation C3a receptor and C5a receptor. Complement activation thus contributes to increased inflammatory cytokine production and can influence redox signaling. Here we will review recent progress in understanding the interactions between oxidative stress and innate immunity in ALD. These data illustrate that ethanol-induced oxidative stress and activation of the innate immune system interact dynamically during ethanol exposure, exacerbating ethanol-induced liver injury.
Figures


References
-
- Adachi Y. Bradford BU. Gao W. Bojes HK. Thurman RG. Inactivation of Kupffer cells prevents early alcohol-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 1994;20:453–460. - PubMed
-
- Arteel GE. Oxidants and antioxidants in alcohol-induced liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:778–790. - PubMed
-
- Balkan J. Parldar FH. Dogru-Abbasoglu S. Aykac-Toker G. Uysal M. The effect of taurine or betaine pretreatment on hepatotoxicity and prooxidant status induced by lipopolysaccharide treatment in the liver of rats. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;17:917–921. - PubMed
-
- Bode JC. Bode G. Heidelbach R. Durr HK. Martini GA. Jejunal microflora in patients with chronic alcohol abuse. Hepatogastroenterology. 1984;31:30–34. - PubMed
-
- Bohana-Kashtan O. Ziporen L. Donin N. Kraus S. Fishelson Z. Cell signals transduced by complement. Mol Immunol. 2004;41:583–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

