Mechanism of cluster DNA damage repair in response to high-atomic number and energy particles radiation
- PMID: 21126526
- PMCID: PMC3318975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.11.002
Mechanism of cluster DNA damage repair in response to high-atomic number and energy particles radiation
Abstract
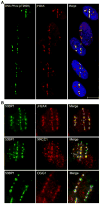
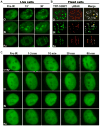
Low-linear energy transfer (LET) radiation (i.e., γ- and X-rays) induces DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) that are rapidly repaired (rejoined). In contrast, DNA damage induced by the dense ionizing track of high-atomic number and energy (HZE) particles is slowly repaired or is irreparable. These unrepaired and/or misrepaired DNA lesions may contribute to the observed higher relative biological effectiveness for cell killing, chromosomal aberrations, mutagenesis, and carcinogenesis in HZE particle irradiated cells compared to those treated with low-LET radiation. The types of DNA lesions induced by HZE particles have been characterized in vitro and usually consist of two or more closely spaced strand breaks, abasic sites, or oxidized bases on opposing strands. It is unclear why these lesions are difficult to repair. In this review, we highlight the potential of a new technology allowing direct visualization of different types of DNA lesions in human cells and document the emerging significance of live-cell imaging for elucidation of the spatio-temporal characterization of complex DNA damage. We focus on the recent insights into the molecular pathways that participate in the repair of HZE particle-induced DSBs. We also discuss recent advances in our understanding of how different end-processing nucleases aid in repair of DSBs with complicated ends generated by HZE particles. Understanding the mechanism underlying the repair of DNA damage induced by HZE particles will have important implications for estimating the risks to human health associated with HZE particle exposure.
2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Letaw JR, Silberberg R, Tsao CH. Radiation hazards on space missions. Nature. 1987;330:709–710. - PubMed
-
- George K, Durante M, Wu H, Willingham V, Badhwar G, Cucinotta FA. Chromosome aberrations in the blood lymphocytes of astronauts after space flight. Radiat Res. 2001;156:731–738. - PubMed
-
- Goodhead DT. New radiobiological, radiation risk and radiation protection paradigms. Mutat Res. 2010;687:13–16. - PubMed
-
- Durante M, Cucinotta FA. Heavy ion carcinogenesis and human space exploration. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:465–472. - PubMed
-
- Curtis SB, Letaw JR. Galactic cosmic rays and cell-hit frequencies outside the magnetosphere. Adv Space Res. 1989;9:293–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

