Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome epidemiology after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
- PMID: 21126596
- PMCID: PMC3061253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.11.018
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome epidemiology after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Abstract
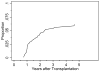
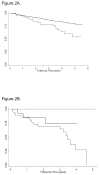
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is a pulmonary complication of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (aHCT). Recent National Institutes of Health consensus diagnostic criteria for BOS have not been assessed in a clinical setting. Modified National Institutes of Health diagnostic consensus criteria for BOS were applied to evaluate its prevalence, risk factors, and outcomes in the modern era of aHCT. Pulmonary function tests from 1145 patients were screened to identify patients with new-onset airflow obstruction. Clinical records were reviewed to exclude pulmonary infection and other causes. The overall prevalence of BOS among all transplanted patients was 5.5%, and 14% among patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD). The median time from transplant to meeting spirometric criteria for BOS was 439 days (range: 274-1690). Although many previously identified risk factors were not significantly associated, lower baseline FEV(1)/FVC ratio (P = .006), non-Caucasian race (P = .014), lower circulating IgG level (P = .010), and presence of cGVHD (P < 0.001) were associated with an increase in risk, with the latter associated with a 10-fold increase in risk. Multivariate analysis indicated that BOS conferred a 1.6-fold increase in risk for mortality after diagnosis. These results suggest that the National Institutes of Health diagnostic criteria can reliably identify BOS, and that it is more prevalent than previously suggested. Spirometric monitoring of high-risk patients with cGVHD may permit earlier detection and intervention for this often-fatal disease.
2011 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Afessa B, Litzow MR, Tefferi A. Bronchiolitis obliterans and other late onset non-infectious pulmonary complications in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001;28:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Dudek AZ, Mahaseth H, DeFor TE, Weisdorf DJ. Bronchiolitis obliterans in chronic graft-versus-host disease: analysis of risk factors and treatment outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003;9:657–666. - PubMed
-
- Clark JG, Schwartz DA, Flournoy N, Sullivan KM, Crawford SW, Thomas ED. Risk factors for airflow obstruction in recipients of bone marrow transplants. Ann Intern Med. 1987;107:648–656. - PubMed
-
- Holland HK, Wingard JR, Beschorner WE, Saral R, Santos GW. Bronchiolitis obliterans in bone marrow transplantation and its relationship to chronic graft-v-host disease and low serum IgG. Blood. 1988;72:621–627. - PubMed
-
- Marras TK, Chan CK, Lipton JH, Messner HA, Szalai JP, Laupacis A. Long-term pulmonary function abnormalities and survival after allogeneic marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004;33:509–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

