ROS and CHOP are critical for dibenzylideneacetone to sensitize tumor cells to TRAIL through induction of death receptors and downregulation of cell survival proteins
- PMID: 21127198
- PMCID: PMC3022089
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3121
ROS and CHOP are critical for dibenzylideneacetone to sensitize tumor cells to TRAIL through induction of death receptors and downregulation of cell survival proteins
Retraction in
-
Retraction: ROS and CHOP Are Critical for Dibenzylideneacetone to Sensitize Tumor Cells to TRAIL through Induction of Death Receptors and Downregulation of Cell Survival Proteins.Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 1;78(17):5185. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2370. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30181309 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
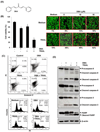
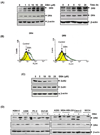
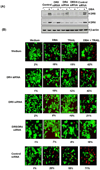
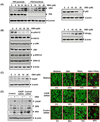
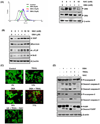
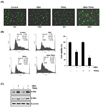
Because tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) selectively kills tumor cells, it is being tested in cancer patients. Unfortunately, patients develop resistance to the cytokine, therefore, agents that can sensitize cells to TRAIL are urgently needed. In this study, we investigated whether dibenzylideneacetone (DBA) can sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL and potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis. As indicated by accumulation of the membrane phospholipid phosphatidylserine, DNA breaks, intracellular esterase activity, and activation of caspase-8, -9, and -3, we concluded that DBA potentiated TRAIL-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. DBA also converted TRAIL resistant-cells to TRAIL-sensitive. When examined for the mechanism, we found that DBA decreased the expression of antiapoptotic proteins and decoy receptor-2 and increased proapoptotic proteins. DBA also induced both death receptor (DR)-5 and DR4. Knockdown of DR5 and DR4 by small interfering RNA (SiRNA) reduced the sensitizing effect of DBA on TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In addition, DBA increased the expression of CHOP proteins. Knockdown of CHOP by siRNA decreased the induction of DBA-induced DR5 expression and apoptosis. Induction of receptors by DBA, however, was p53-independent, as deletion of p53 had no effect on receptor induction. We observed that DBA-induced induction of DR5 and DR4 was mediated through generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), as N-acetylcysteine blocked the induction of death receptors and suppression of cell survival proteins by DBA. Overall, our results show that DBA potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis through downregulation of cell survival proteins and upregulation of death receptors via activation of ROS and CHOP mediated pathways.
© 2010 AACR.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Plummer R, Attard G, Pacey S, et al. Phase 1 and pharmacokinetic study of lexatumumab in patients with advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:6187–6194. - PubMed
-
- Hotte SJ, Hirte HW, Chen EX, et al. A phase 1 study of mapatumumab (fully human monoclonal antibody to TRAIL-R1) in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:3450–3455. - PubMed
-
- Camidge DR, Herbst RS, Gordon MS, et al. A phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of the death receptor 5 agonistic antibody PRO95780 in patients with advanced malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1256–1263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

