Adrenergic signaling in human oral keratinocytes and wound repair
- PMID: 21127260
- PMCID: PMC3144102
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034510388034
Adrenergic signaling in human oral keratinocytes and wound repair
Abstract
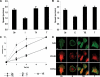
Catecholamines are present in saliva, but their influence on oral epithelium is not understood. Because psychological stress increases salivary catecholamines and impairs oral mucosal wound healing, we sought to determine if epithelial adrenergic signaling could link these two findings. We found that cultured human oral keratinocytes (HOK) express the α(2B)- and β(2)-adrenergic receptors (ARs). Exposure of HOK to either epinephrine or the β-AR agonist, isoproterenol, reduced migratory speed and decreased in vitro scratch wound healing. Incubation with the β-AR antagonist timolol reversed the catecholamine-induced effects, indicating that the observed response is mediated by β-AR. Epinephrine treatment decreased phosphorylation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) ERK1/2 and p38; these decreases were also reversed with timolol. Cultured HOK express enzymes of the epinephrine synthetic pathway, and generate epinephrine. These findings demonstrate that stress-induced elevations of salivary catecholamines signal through MAPK pathways, and result in impaired oral keratinocyte migration required for healing.
Figures

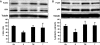

References
-
- Albanidou-Farmaki E, Poulopoulos AK, Epivatianos A, Farmakis K, Karamouzis M, Antoniades D. (2008). Increased anxiety level and high salivary and serum cortisol concentrations in patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Tohoku J Exp Med 214:291-296 - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Hoffman BB, Isseroff RR. (2002). Beta-adrenergic receptor activation inhibits keratinocyte migration via a cyclic adenosine monophosphate-independent mechanism. J Invest Dermatol 119:1261-1268 - PubMed
-
- Fitsialos G, Chassot AA, Turchi L, Dayem MA, LeBrigand K, Moreilhon C, et al. (2007). Transcriptional signature of epidermal keratinocytes subjected to in vitro scratch wounding reveals selective roles for ERK1/2, p38, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 282:15090-15102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

