Apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site recognition by the 5'-dRP/AP lyase in poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1)
- PMID: 21127267
- PMCID: PMC3009834
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1009182107
Apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site recognition by the 5'-dRP/AP lyase in poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1)
Abstract
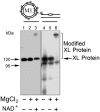
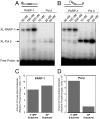
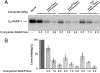
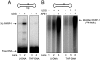
The capacity of human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) to interact with intact apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites in DNA has been demonstrated. In cell extracts, sodium borohydride reduction of the PARP-1/AP site DNA complex resulted in covalent cross-linking of PARP-1 to DNA; the identity of cross-linked PARP-1 was confirmed by mass spectrometry. Using purified human PARP-1, the specificity of PARP-1 binding to AP site-containing DNA was confirmed in competition binding experiments. PARP-1 was only weakly activated to conduct poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis upon binding to AP site-containing DNA, but was strongly activated for poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis upon strand incision by AP endonuclease 1 (APE1). By virtue of its binding to AP sites, PARP-1 could be poised for its role in base excision repair, pending DNA strand incision by APE1 or the 5'-dRP/AP lyase activity in PARP-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature. 1993;362:709–715. - PubMed
-
- McCullough AK, Dodson ML, Lloyd RS. Initiation of base excision repair: Glycosylase mechanisms and structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:255–285. - PubMed
-
- Burrows CJ, Muller JG. Oxidative nucleobase modifications leading to strand scission. Chem Rev. 1998;98:1109–1152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

