Genetic variation in LPAL2, LPA, and PLG predicts plasma lipoprotein(a) level and carotid artery disease risk
- PMID: 21127300
- PMCID: PMC3020902
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.591230
Genetic variation in LPAL2, LPA, and PLG predicts plasma lipoprotein(a) level and carotid artery disease risk
Abstract
Background and purpose: lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] level is an established risk factor for coronary artery disease and has been implicated in carotid artery disease (CAAD). The relationship between genetic variation in the LPA gene region and CAAD risk remains unknown.
Methods: we genotyped single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the LPAL2, LPA, and PLG regions in 530 individuals with severe CAAD and 770 controls and kringle IV type 2 (KIV2) repeat length in a subset of 90 individuals.
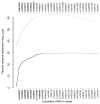
Results: nine SNPs collectively accounted for 30% of the variance in Lp(a) level. Six SNPs were associated with Lp(a) level after accounting for KIV2 copy number, and the dominant KIV2 allele combined with these markers explained 60% of the variance in Lp(a) level. Five SNPs, including rs10455872, which had an odds ratio of 2.1 per minor allele and haplotypes formed by rs10455872, rs6919346, and rs3123629, were significant predictors of CAAD. After accounting for Lp(a) level, all evidence of CAAD-genotype association in the LPA region was eliminated.
Conclusions: LPA region SNPs capture some but not all of the effect of KIV2 repeat length on Lp(a) level. There are associations between LPA region SNPs and CAAD that appear to be attributable to effects on Lp(a) level.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Goldstein LB, Adams R, Alberts MJ, Appel LJ, Brass LM, Bushnell CD, Culebras A, Degraba TJ, Gorelick PB, Guyton JR, Hart RG, Howard G, Kelly-Hayes M, Nixon JV, Sacco RL. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: A guideline from the american heart association/american stroke association stroke council: Cosponsored by the atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease interdisciplinary working group; cardiovascular nursing council; clinical cardiology council; nutrition, physical activity, and metabolism council; and the quality of care and outcomes research interdisciplinary working group: The american academy of neurology affirms the value of this guideline. Stroke. 2006;37:1583–1633. - PubMed
-
- Samuelson RM, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Hopkins LN. The cost of stroke prevention. Stroke. 2009;40:e41–42. author reply e43. - PubMed
-
- North KE, MacCluer JW, Devereux RB, Howard BV, Welty TK, Best LG, Lee ET, Fabsitz RR, Roman MJ. Heritability of carotid artery structure and function: The strong heart family study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:1698–1703. - PubMed
-
- Zannad F, Visvikis S, Gueguen R, Sass C, Chapet O, Herbeth B, Siest G. Genetics strongly determines the wall thickness of the left and right carotid arteries. Hum Genet. 1998;103:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Jartti L, Ronnemaa T, Kaprio J, Jarvisalo MJ, Toikka JO, Marniemi J, Hammar N, Alfredsson L, Saraste M, Hartiala J, Koskenvuo M, Raitakari OT. Population-based twin study of the effects of migration from finland to sweden on endothelial function and intima-media thickness. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:832–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

