zVAD-induced autophagic cell death requires c-Src-dependent ERK and JNK activation and reactive oxygen species generation
- PMID: 21127402
- PMCID: PMC3039770
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.7.2.14212
zVAD-induced autophagic cell death requires c-Src-dependent ERK and JNK activation and reactive oxygen species generation
Abstract
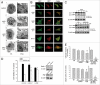
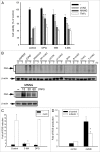
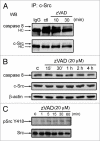
The treatment of L929 fibrosarcoma cells with zVAD has been shown to induce necroptosis. However, whether autophagy is involved or not in this event remains controversial. In this study, we re-examined the role of autophagy in zVAD-induced cell death in L929 cells and further elucidated the signaling pathways triggered by caspase inhibition and contributing to autophagic death. First, we found that zVAD can stimulate LC3-II formation, autophagosome and autolysosome formation, and ROS accumulation. Antioxidants, beclin 1 or Atg5 silencing, and class III PtdIns3K inhibitors all effectively blocked ROS production and cell death, suggesting ROS accumulation downstream of autophagy contributes to cell necrosis. zVAD also stimulated PARP activation, and the PARP inhibitor DPQ can reduce zVAD-induced cell death, but did not affect ROS production, suggesting the increased ROS leads to PARP activation and cell death. Notably, our data also indicated the involvement of Src-dependent JNK and ERK in zVAD-induced ROS production and autophagic death. We found caspase 8 is associated with c-Src at the resting state, and upon zVAD treatment this association was decreased and accompanied by c-Src activation. In conclusion, we confirm the autophagic death in zVAD-treated L929 cells, and define a new molecular pathway in which Src-dependent ERK and JNK activation can link a signal from caspase inhibition to autophagy, which in turn induce ROS production and PARP activation, eventually leading to necroptosis. Thus, in addition to initiating proteolytic activity for cell apoptosis, inactivated caspase 8 also functions as a signaling molecule for autophagic death.
Figures



Comment in
-
New thoughts regarding Atg8 and ubiquitination.Autophagy. 2011 Feb;7(2):125-6. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.2.14428. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Autophagy. 2011. PMID: 21160277 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cinobufagin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells through the ROS/JNK/p38 signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):90-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4782. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Oncol Rep. 2016. Retraction in: Oncol Rep. 2025 Aug;54(2):95. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8928. PMID: 27176794 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Modulation of ROS/MAPK signaling pathways by okadaic acid leads to cell death via, mitochondrial mediated caspase-dependent mechanism.Apoptosis. 2011 Feb;16(2):145-61. doi: 10.1007/s10495-010-0554-0. Apoptosis. 2011. PMID: 21082355
-
zVAD-induced necroptosis in L929 cells depends on autocrine production of TNFα mediated by the PKC-MAPKs-AP-1 pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Jan;18(1):26-37. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.72. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 20539307 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase inhibitors promote alternative cell death pathways.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 24;2006(358):pe44. doi: 10.1126/stke.3582006pe44. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17062895 Review.
-
The mechanisms of graphene-based materials-induced programmed cell death: a review of apoptosis, autophagy, and programmed necrosis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Sep 7;12:6633-6646. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S140526. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28924347 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autosis and autophagic cell death: the dark side of autophagy.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Mar;22(3):367-76. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.143. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25257169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing of Programmed Necrosis for Fighting against Cancers.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014 May;22(3):167-75. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2014.046. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014. PMID: 25009696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAK1 mediates excessive autophagy via p38 and ERK in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 May;22(5):2908-2921. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13585. Epub 2018 Mar 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29504713 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein Degradation in Brain Pericytes Is Mediated via Akt, ERK, and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 14;26(4):1615. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041615. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004079 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinsonian toxin-induced oxidative stress inhibits basal autophagy in astrocytes via NQO2/quinone oxidoreductase 2: Implications for neuroprotection.Autophagy. 2015;11(7):1063-80. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1058683. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 26046590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–219. - PubMed
-
- Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G. Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:741–752. - PubMed
-
- Hippert MM, O'Toole PS, Thorburn A. Autophagy in cancer: good, bad or both? Cancer Res. 2006;66:9349–9351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
