Spontaneous dissection of right coronary artery manifested with acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 21127744
- PMCID: PMC2995159
- DOI: 10.2174/1874192401004010178
Spontaneous dissection of right coronary artery manifested with acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
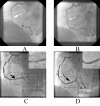
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection is a rare cause of acute ischemic coronary events and sudden cardiac death. It usually occurs in young women without traditional risk factors for coronary artery disease during pregnancy or postpartum period. However, it has also been reported in patients with atherosclerotic coronary disease. We present a case of spontaneous right coronary artery dissection in a 48-year male with recent myocardial infarction and previous percutaneous coronary intervention.
Keywords: Coronary artery dissection; atherosclerosis..
Figures
Similar articles
-
A rare case of stenting of spontaneous dissection of Shepherd's Crook right coronary artery.ARYA Atheroscler. 2014 Mar;10(2):129-32. ARYA Atheroscler. 2014. PMID: 25161681 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection diagnosed by multislice computed tomography.Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2013;9(1):111-3. doi: 10.5114/pwki.2013.34038. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2013. PMID: 24570701 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy and the Risk of Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection: An Analysis of 120 Contemporary Cases.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 Mar;10(3):e004941. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.117.004941. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2017. PMID: 28302642 Review.
-
A woman complicated by sudden cardiac arrest owing to spontaneous coronary artery dissection after stillbirth.J Cardiol Cases. 2020 Oct 10;23(2):61-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2020.09.009. eCollection 2021 Feb. J Cardiol Cases. 2020. PMID: 33520024 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection: case report and literature review.J Forensic Sci. 2015 May;60(3):801-6. doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.12722. Epub 2015 Feb 10. J Forensic Sci. 2015. PMID: 25678077 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Coronary Syndrome in Pre- and Post-partum Women - A Review.Interv Cardiol. 2013 Mar;8(1):8-13. doi: 10.15420/icr.2013.8.1.8. Interv Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 29588744 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Idiopathic Dissections of the Coronary and Superior Mesenteric Arteries.Intern Med. 2017;56(11):1363-1367. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.8043. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28566599 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection mimicking coronary spasm diagnosed by intravascular ultrasonography.Korean Circ J. 2013 Jul;43(7):491-6. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2013.43.7.491. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Korean Circ J. 2013. PMID: 23964297 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD): A Series of 7 Cases, Experience of the University Hospital Center Mohammed VI, Oujda, Morocco.Adv Med. 2018 Oct 2;2018:1964394. doi: 10.1155/2018/1964394. eCollection 2018. Adv Med. 2018. PMID: 30386796 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection: a case series and literature review.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2014 Sep 29;4(4). doi: 10.3402/jchimp.v4.25261. eCollection 2014. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2014. PMID: 25317273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mortensen KH, Thuesen L, Kristensen IB, Christiansen EH. Spontaneous coronary artery dissection: a Western Denmark Heart Registry study. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;74:710–7. - PubMed
-
- Azzarelli S, Fiscella D, Amico F, Giacoppo M, Argentino V, Fiscella A. Multivessel spontaneous coronary artery dissection in a postpartum woman treated with multiple drug-eluting stents. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2009;10:340–3. - PubMed
-
- Hayes CR, Lewis D. Spontaneous coronary artery dissection of the left circumflex artery causing cardiac tamponade and presenting with atrial fibrillation: a case report and review of the literature. Angiology. 2007;58:630–5. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen MB, Aharonian V, Mansukhani P, Mahrer PR. Spontaneous coronary dissection: a cluster of cases with this rare finding. Am Heart J. 1994;127:1382–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
