Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 21128705
- PMCID: PMC3118611
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3790
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
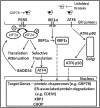
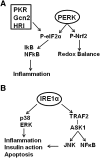
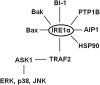
The underlying causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are unclear, although recent evidence has implicated the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in both the development of steatosis and progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Disruption of ER homeostasis, often termed "ER stress," has been observed in liver and adipose tissue of humans with NAFLD and/or obesity. Importantly, the signaling pathway activated by disruption of ER homeostasis, the unfolded protein response, has been linked to lipid biosynthesis, insulin action, inflammation, and apoptosis. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms that disrupt ER homeostasis in NAFLD and the role of ER-mediated signaling have become topics of intense investigation. The present review will examine the ER and the unfolded protein response in the context of NAFLD.
Figures



Comment in
-
Emerging role of redox dysregulation in alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Jul 15;15(2):421-4. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.3897. Epub 2011 May 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 21254858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aigner E. Theurl I. Theurl M. Lederer D. Haufe H. Dietze O. Strasser M. Datz C. Weiss G. Pathways underlying iron accumulation in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:1374–1383. - PubMed
-
- Allard JP. Aghdassi E. Mohammed S. Raman M. Avand G. Arendt BM. Jalali P. Kandasamy T. Prayitno N. Sherman M. Guindi M. Ma DWL. Heathcote JE. Nutritional assessment and hepatic fatty acid composition in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a cross-sectional study. J Hepatol. 2008;48:300–307. - PubMed
-
- Alpini G. Kanno N. Phinizy JL. Glaser S. Francis H. Taffetani S. LeSage G. Tauroursodeoxycholate inhibits human cholangiocarcinoma growth via calcium-, PKC-, and MAPK-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G973–G982. - PubMed
-
- Argo CK. Caldwell SH. Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis. 2009;13:511–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

