The dominant Anopheles vectors of human malaria in Africa, Europe and the Middle East: occurrence data, distribution maps and bionomic précis
- PMID: 21129198
- PMCID: PMC3016360
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-3-117
The dominant Anopheles vectors of human malaria in Africa, Europe and the Middle East: occurrence data, distribution maps and bionomic précis
Abstract
Background: This is the second in a series of three articles documenting the geographical distribution of 41 dominant vector species (DVS) of human malaria. The first paper addressed the DVS of the Americas and the third will consider those of the Asian Pacific Region. Here, the DVS of Africa, Europe and the Middle East are discussed. The continent of Africa experiences the bulk of the global malaria burden due in part to the presence of the An. gambiae complex. Anopheles gambiae is one of four DVS within the An. gambiae complex, the others being An. arabiensis and the coastal An. merus and An. melas. There are a further three, highly anthropophilic DVS in Africa, An. funestus, An. moucheti and An. nili. Conversely, across Europe and the Middle East, malaria transmission is low and frequently absent, despite the presence of six DVS. To help control malaria in Africa and the Middle East, or to identify the risk of its re-emergence in Europe, the contemporary distribution and bionomics of the relevant DVS are needed.
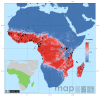
Results: A contemporary database of occurrence data, compiled from the formal literature and other relevant resources, resulted in the collation of information for seven DVS from 44 countries in Africa containing 4234 geo-referenced, independent sites. In Europe and the Middle East, six DVS were identified from 2784 geo-referenced sites across 49 countries. These occurrence data were combined with expert opinion ranges and a suite of environmental and climatic variables of relevance to anopheline ecology to produce predictive distribution maps using the Boosted Regression Tree (BRT) method.
Conclusions: The predicted geographic extent for the following DVS (or species/suspected species complex*) is provided for Africa: Anopheles (Cellia) arabiensis, An. (Cel.) funestus*, An. (Cel.) gambiae, An. (Cel.) melas, An. (Cel.) merus, An. (Cel.) moucheti and An. (Cel.) nili*, and in the European and Middle Eastern Region: An. (Anopheles) atroparvus, An. (Ano.) labranchiae, An. (Ano.) messeae, An. (Ano.) sacharovi, An. (Cel.) sergentii and An. (Cel.) superpictus*. These maps are presented alongside a bionomics summary for each species relevant to its control.
Figures
References
-
- Hay SI, Sinka ME, Okara RM, Kabaria CW, Mbithi PM, Tago CT, Benz D, Gething PW, Howes RE, Patil AP, Temperley WH, Bangs MJ, Chareonviriyaphap T, Elyazar IRF, Harbach RE, Hemingway J, Manguin S, Mbogo CM, Rubio-Palis Y, Godfray HCJ. Developing global maps of the dominant Anopheles vectors of human malaria. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sinka ME, Rubio-Palis Y, Manguin S, Patil AP, Temperley WH, Gething PW, Van Boeckel T, Kabaria CW, Harbach RE, Hay SI. The dominant Anopheles vectors of human malaria in the Americas: occurrence data, distribution maps and bionomic précis. Parasit Vectors. 2010;3:72. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-3-72. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

