The roles of Akt and NOSs in regulation of VLA-4-mediated melanoma cell adhesion to endothelial VCAM-1 after UVB-irradiation
- PMID: 21129359
- PMCID: PMC3073699
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.11.021
The roles of Akt and NOSs in regulation of VLA-4-mediated melanoma cell adhesion to endothelial VCAM-1 after UVB-irradiation
Abstract
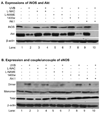
UVB-reduced avidity between M624 melanoma and HUVEC cells is dependent on the interaction of VLA-4 with its endothelial ligand VCAM-1. Our previous studies suggested that a spatial organization of α4 integrin, one of the two subunits of VLA-4, on the melanoma cell surface contributed to the changes in avidity for VCAM-1 upon UVB-irradiation. In this study, we demonstrate that Akt plays an important role in regulation of the expression and surface level of α4 integrin on melanoma cells upon UVB-irradiation. While the cell surface level of α4 integrin is not significantly affected by UVB-irradiation or Akt inhibitor alone, it is dynamically altered after UVB-irradiation when Akt is inhibited. Inhibition of Akt also reverses the reduction of avidity of cells after the irradiation. Our data also shows that UVB reduces the level of Akt. The inhibition of Akt activity correlates with a reduced amount of coupled cNOS and reduced amount of iNOS after UVB-irradiation. However, the effect of NOSs on melanoma cell adhesion appears due to their roles in regulation of apoptosis after UVB-irradiation. Base on these results, we propose that the UVB-induced reduction of avidity of melanoma cells is coordinatively regulated by NOSs and Akt through two differential mechanisms.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

