Limited activity monitoring in toddlers with autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 21129365
- PMCID: PMC3050079
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.11.074
Limited activity monitoring in toddlers with autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
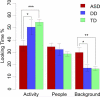
This study used eye-tracking to examine how 20-month-old toddlers with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) (n=28), typical development (TD) (n=34), and non-autistic developmental delays (DD) (n=16) monitored the activities occurring in a context of an adult-child play interaction. Toddlers with ASD, in comparison to control groups, showed less attention to the activities of others and focused more on background objects (e.g., toys). In addition, while all groups spent the same time overall looking at people, toddlers with ASD looked less at people's heads and more at their bodies. In ASD, these patterns were associated with cognitive deficits and greater autism severity. These results suggest that the monitoring of the social activities of others is disrupted early in the developmental progression of autism, limiting future avenues for observational learning.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abravanel E, Levan-Goldschmidt E, Stevenson MB. Action Imitation: The Early Phase of Infancy. Child Development. 1976;47:1032–1044. - PubMed
-
- ActiveState ActivePerl (Version 5.10) [Computer Software] 2009. Available at: http://www.activestate.com/activeperl/
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fourth ed., text revision American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000.
-
- Anderson CJ, Colombo J, Shaddy DJ. Visual Scanning and Pupillary Responses in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 2006;28:1238–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

