Prevalence of tobacco use and association between cardiometabolic risk factors and cigarette smoking in youth with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 21129757
- PMCID: PMC3908882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.10.011
Prevalence of tobacco use and association between cardiometabolic risk factors and cigarette smoking in youth with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objectives: To examine prevalence of tobacco use and coexistence of cardiometabolic risk factors according to smoking status in youth with diabetes mellitus.
Study design: Youth aged 10 to 22 years who participated in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study (n = 3466) were surveyed about their tobacco use and examined for cardiometabolic risk factors: waist circumference, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, physical activity, and lipid profile.
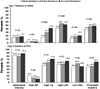
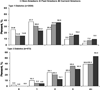
Results: The prevalence of tobacco use in youth aged 10 to 14 years, 15 to 19 years, and ≥20 years with type 1 diabetes mellitus was 2.7%, 17.1%, and 34.0%, respectively, and the prevalence in youth with type 2 diabetes mellitus was 5.5%, 16.4%, and 40.3%, respectively. Smoking was more likely in youth with annual family incomes <$50 000, regardless of diabetes mellitus type. Cigarette smoking was associated with higher odds of high triglyceride levels and physical inactivity in youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Less than 50% of youth aged 10 to 14 years (52.2% of participants) reported having ever been counseled by their healthcare provider to not smoke or to stop smoking.
Conclusions: Tobacco use is prevalent in youth with diabetes mellitus. Aggressive tobacco prevention and cessation programs should be a high priority to prevent or delay the development of cardiovascular disease.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding support and conflict of interest information is available at
Figures
Comment in
-
The challenge of communicating cardiovascular risk information to our patients.J Pediatr. 2011 Apr;158(4):527-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.11.031. Epub 2011 Jan 15. J Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 21238985 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ezzati M, Lopez AD. Estimates of global mortality attributable to smoking in 2000. Lancet. 2003;362:847–852. - PubMed
-
- Haire-Joshu D, Glasgow RE, Tibbs TL. Smoking and diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:1887–1898. - PubMed
-
- Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton JD, Wentworth D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:434–444. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and glucose tolerance as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. Diabetes Care. 1979;2:120–126. - PubMed
-
- Moy CS, LaPorte RE, Dorman JS, Songer TJ, Orchard TJ, Kuller LH, et al. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus mortality. The risk of cigarette smoking. Circulation. 1990;82:37–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

