Exploiting bacterial peptide display technology to engineer biomaterials for neural stem cell culture
- PMID: 21129772
- PMCID: PMC3010314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.032
Exploiting bacterial peptide display technology to engineer biomaterials for neural stem cell culture
Abstract
Stem cells are often cultured on substrates that present extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins; however, the heterogeneous and poorly defined nature of ECM proteins presents challenges both for basic biological investigation of cell-matrix investigations and translational applications of stem cells. Therefore, fully synthetic, defined materials conjugated with bioactive ligands, such as adhesive peptides, are preferable for stem cell biology and engineering. However, identifying novel ligands that engage cellular receptors can be challenging, and we have thus developed a high throughput approach to identify new adhesive ligands. We selected an unbiased bacterial peptide display library for the ability to bind adult neural stem cells (NSCs), and 44 bacterial clones expressing peptides were identified and found to bind to NSCs with high avidity. Of these clones, four contained RGD motifs commonly found in integrin binding domains, and three exhibited homology to ECM proteins. Three peptide clones were chosen for further analysis, and their synthetic analogs were adsorbed on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) or grafted onto an interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) for cell culture. These three peptides were found to support neural stem cell self-renewal in defined medium as well as multi-lineage differentiation. Therefore, bacterial peptide display offers unique advantages to isolate bioactive peptides from large, unbiased libraries for applications in biomaterials engineering.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



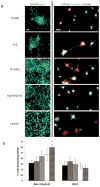
 ) TCPS alone, were dissolved at 100 μM in synthesis-grade water or DMSO for 15-2, and then peptides were dried on TCPS. (a). Brightfield micrographs of the neural stem cells after 4 days of culture on the adsorbed surfaces exhibited similar attachment and clumping of cells on the surface on the 7C-9(9), 7C-24(9), 15-2, and bsp-RGD(15) surfaces, while the bsp-RGE(15) and TCPS surfaces had significantly fewer cells. The scale bar represents 250 μm. (b) Quantification of the number of cells on the surface with the Cyquant cell counting assay showed similar numbers of cells on all surfaces except the bsp-RGE(15) and TCPS surfaces, which had significantly fewer cells. (c) NSCs grown under differentiating conditions were assessed for expression of GFAP (red), a cytoskeletal marker for astrocytes, and β-Tubulin III (green), a cytoskeletal marker for neurons. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). All peptide surfaces had both astrocytes and neurons under differentiating conditions. All scale bars represent 100 μm. (d) Quantification of differentiation markers, β-Tubulin III and GFAP, on peptide-adsorbed surfaces. All library-selected and bsp-RGD(15) peptide surfaces had similar percentages of neurons and astrocytes compared to laminin, while bsp-RGE(15) and TCPS surfaces had fewer neurons and more astrocytes. (Data represent mean ± standard deviation. Library populations not in the same group (*) were statistically different from one another (p < 0.05 using ANOVA between groups with Tukey-Kramer significant difference post hoc test).
) TCPS alone, were dissolved at 100 μM in synthesis-grade water or DMSO for 15-2, and then peptides were dried on TCPS. (a). Brightfield micrographs of the neural stem cells after 4 days of culture on the adsorbed surfaces exhibited similar attachment and clumping of cells on the surface on the 7C-9(9), 7C-24(9), 15-2, and bsp-RGD(15) surfaces, while the bsp-RGE(15) and TCPS surfaces had significantly fewer cells. The scale bar represents 250 μm. (b) Quantification of the number of cells on the surface with the Cyquant cell counting assay showed similar numbers of cells on all surfaces except the bsp-RGE(15) and TCPS surfaces, which had significantly fewer cells. (c) NSCs grown under differentiating conditions were assessed for expression of GFAP (red), a cytoskeletal marker for astrocytes, and β-Tubulin III (green), a cytoskeletal marker for neurons. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). All peptide surfaces had both astrocytes and neurons under differentiating conditions. All scale bars represent 100 μm. (d) Quantification of differentiation markers, β-Tubulin III and GFAP, on peptide-adsorbed surfaces. All library-selected and bsp-RGD(15) peptide surfaces had similar percentages of neurons and astrocytes compared to laminin, while bsp-RGE(15) and TCPS surfaces had fewer neurons and more astrocytes. (Data represent mean ± standard deviation. Library populations not in the same group (*) were statistically different from one another (p < 0.05 using ANOVA between groups with Tukey-Kramer significant difference post hoc test).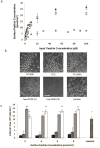
Similar articles
-
Tethered growth factors on biocompatible scaffolds improve stemness of cultured rat and human neural stem cells and growth of oligodendrocyte progenitors.Methods. 2018 Jan 15;133:54-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Methods. 2018. PMID: 28887084
-
Extracellular matrix mimetic peptide scaffolds for neural stem cell culture and differentiation.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1202:131-48. doi: 10.1007/7651_2013_35. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24519002
-
Expansion and differentiation of human neural stem cells on synthesized integrin binding peptide surfaces.Biomed Mater. 2024 Jun 18;19(4). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ad4e85. Biomed Mater. 2024. PMID: 38772389
-
The influence of microenvironment and extracellular matrix molecules in driving neural stem cell fate within biomaterials.Brain Res Bull. 2019 May;148:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30898579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering.Nat Biotechnol. 2005 Jan;23(1):47-55. doi: 10.1038/nbt1055. Nat Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 15637621 Review.
Cited by
-
A robust vitronectin-derived peptide for the scalable long-term expansion and neuronal differentiation of human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived neural progenitor cells (hNPCs).Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 15;48:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.037. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27989923 Free PMC article.
-
Toward discovering a novel family of peptides targeting neuroinflammatory states of brain microglia and astrocytes.J Neurochem. 2024 Oct;168(10):3386-3414. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15840. Epub 2023 Jun 14. J Neurochem. 2024. PMID: 37171455
-
Detection of IP-10 protein marker in undiluted blood serum via an electrochemical E-DNA scaffold sensor.Analyst. 2013 Oct 7;138(19):5580-3. doi: 10.1039/c3an01079a. Analyst. 2013. PMID: 23905162 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-automated Biopanning of Bacterial Display Libraries for Peptide Affinity Reagent Discovery and Analysis of Resulting Isolates.J Vis Exp. 2017 Dec 6;(130):56061. doi: 10.3791/56061. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 29286465 Free PMC article.
-
Microarrayed Materials for Stem Cells.Mater Today (Kidlington). 2012 Oct 1;15(10):10.1016/S1369-7021(12)70196-7. doi: 10.1016/S1369-7021(12)70196-7. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2012. PMID: 24311967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmer TD, Takahashi J, Gage FH. The adult rat hippocampus contains primordial neural stem cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1997;8:389–404. - PubMed
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–7. - PubMed
-
- Campos LS. Beta1 integrins and neural stem cells: making sense of the extracellular environment. Bioessays. 2005;27:698–707. - PubMed
-
- Leiss M, Beckmann K, Giros A, Costell M, Fassler R. The role of integrin binding sites in fibronectin matrix assembly in vivo. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:502–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

